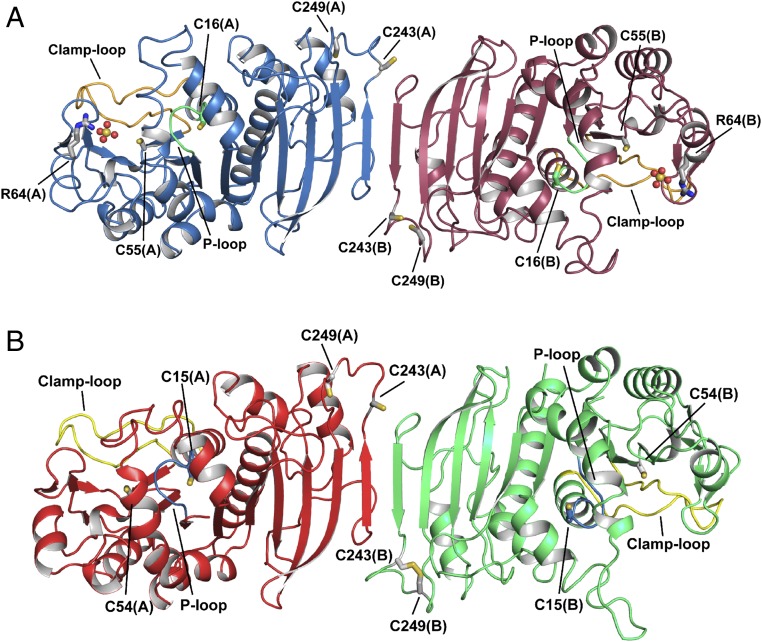
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of photosynthetic PRK. Representation of the overall crystal structure of reduced phosphoribulokinase from (A) C. reinhardtii and (B) A. thaliana. The P loop is highlighted in green and light blue, and the clamp loop in orange and yellow, respectively. Each monomer contains two pairs of cysteines, one in the active site (Cys16 and Cys55 for CrPRK, and Cys15 and Cys54 for AtPRK) and one in the dimer interface close to the C-terminal end of the protein chain (Cys243 and Cys249). Cysteine residues are indicated and represented as sticks. In AtPRK, a pair of C-terminal cysteines forms a disulfide bond. CrPRK binds two sulfate ions (one for each monomer), represented as spheres, from the crystallization solution. Arg64, represented as sticks, is one of the residues stabilizing the anions.