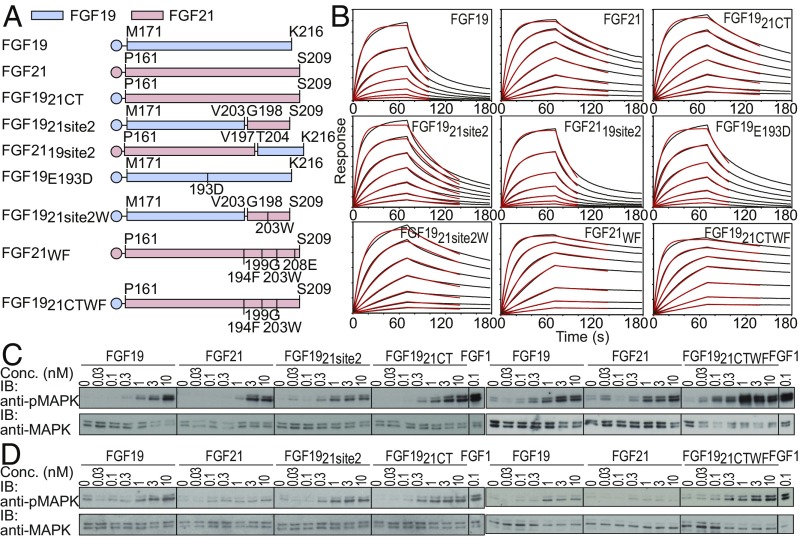
Fig. 3.
Binding parameters and cellular activities of FGF19, FGF21, and their chimeric variants. (A) Schematic diagram of FGF19, FGF21, and their variants tested for their binding affinity, kinetic parameters, and abilities to stimulate MAPK responses. Sequences derived from FGF19 and FGF21 are shown in light blue and light red, respectively. (B) Sensorgrams from BLI measurements. Biosensors coated with anti-histidine antibody were used to capture hexa-histidine–tagged FGF19 or FGF21 variants and dipped into solutions containing a series of concentrations of sKLB (400, 200, 100, 50, 25, 12.5, and 6.25 nM). Sensorgrams were fitted with a 1:1 ligand:receptor–binding model (red lines) to calculate kinetic parameters. (C and D) Comparison of MAPK responses of FGF19, FGF21, and their chimeric ligands. Stably transfected L6 cells expressing either (C) FGFR1c or (D) FGFR4 together with β-Klotho were incubated with various concentrations of FGF19, FGF21, or their chimeric proteins for 10 min and analyzed for MAPK activation.