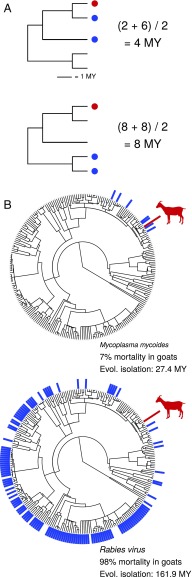
Fig. 2.
(A) Example of how host evolutionary isolation is calculated. Red circles indicate the infected host; blue circles indicate documented hosts. Host evolutionary isolation is calculated as the mean phylogenetic distance from the infected host to all documented host species. (B) Examples with Mycoplasma mycoides and rabies virus. Documented hosts are indicated by blue bars on the host phylogeny, with host evolutionary isolation (Evol. isolation) and average mortality calculated for goats (Capra hircus; shown in red).