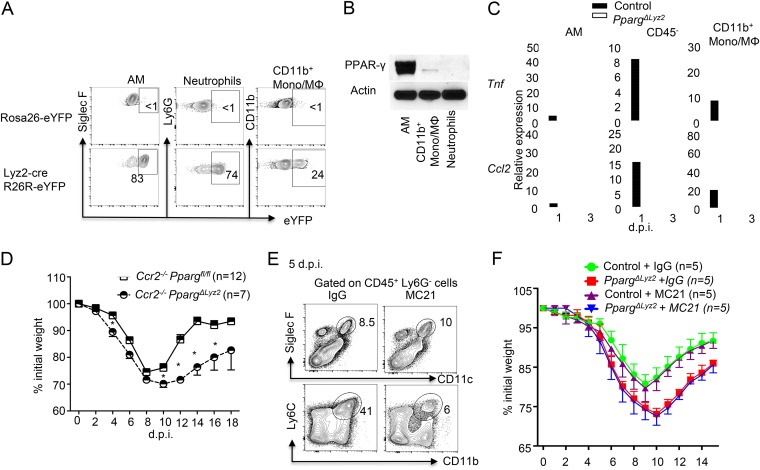
FIG 5.
PPAR-γ expression in resident alveolar macrophages is likely required for the suppression of host morbidity. (A) Lyz2-cre gene recombination in AM, neutrophils, and CD11b+ monocytes/macrophages reported as percent enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (eYFP) expression following crossing with R26R-eYFP reporter mice. (B) Western blot analysis of PPAR-γ protein expression in sorted AM, CD11b+ monocytes/macrophages, and neutrophils in the lungs of naive WT mice (pooled from 3 mice). (C) Tnf and Ccl2 expression in the indicated cell populations in the lungs of control (Ppargfl/fl) or PpargΔLyz2 mice at days 1 and 3 postinfection. (pooled from 2 to 3 mice per group). (D) Ccr2−/− Ppargfl/fl and Ccr2−/− PpargΔLyz2 mice were infected with IAV. Host morbidity (percent initial weight) was monitored. (E) WT mice were infected with IAV and treated with control IgG or mAb MC21. Percentages of lung AM (top panel) and monocytes (bottom panel) in CD45+ Ly6G− cells at 5 dpi. (F) Control (Ppargfl/fl) and PpargΔLyz2 mice were infected with IAV and treated with control IgG or MC21 mAb. Host morbidity (percent initial weight) was monitored. Data are representative of results from at least two to three independent experiments, except for panels C (pooled data from 3 experiments) and D. *, P < 0.05.