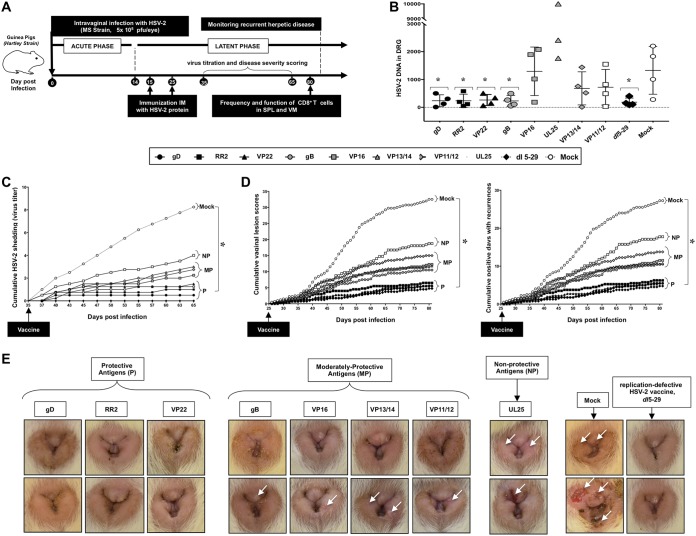
FIG 2.
Protection against recurrent genital herpes infection and disease in HSV-2-infected guinea pigs following therapeutic immunization with eight protein-based subunit vaccine candidates: (A) Timeline of HSV-2 infection, immunization, and immunological and virological analyses. Guinea pigs (n = 60) were infected intravaginally on day 0 with 5 × 105 PFU of HSV-2 (strain MS). Once acute infection was resolved, the remaining latently infected animals were randomly divided into 8 groups (n = 4) and then vaccinated intramuscularly twice, on day 15 and on day 25 postinfection, with 10 μg of the indicated HSV-2 protein-based subunit vaccines (gD, RR2, VP22, gB, VP16, VP13/14, VP11/12, and UL25) emulsified in alum plus CpG adjuvants. The replication-defective HSV-2 dl5-29 mutant vaccine was used as a positive control. Mock-vaccinated guinea pigs which received alum plus CpG adjuvants alone were used as negative control. From day 35 to day 80 postinfection (i.e., day 10 to day 55 after the final immunization), vaccinated and nonvaccinated animals were observed daily for the severity of genital herpetic lesions, scored on a scale of 0 to 4, and pictures of genital areas were taken; vaginal swabs were collected daily from day 35 to day 65 postinfection (i.e., day 10 to day 40 after the final immunization) to detect virus shedding and to quantify HSV-2 DNA copy numbers. (B) HSV-2 DNA copy numbers detected in the DRG of each group of vaccinated and mock-vaccinated guinea pigs. (C) Cumulative vaginal shedding of HSV-2 during recurrent infection. (D) Cumulative vaginal lesions (left) and cumulative positive days with recurrent genital lesions (right). The severity of genital herpetic lesions was scored on a scale of 0 to 4, where 0 reflects no disease, 1 reflects redness, 2 reflects a single lesion, 3 reflects coalesced lesions, and 4 reflects ulcerated lesions. (E) Representative images of genital lesions in guinea pigs vaccinated with (i) protective antigens (gD, RR2, and VP22 proteins), (ii) moderately protective antigens (gB, VP16, VP13/14, and VP11/12), and (iii) nonprotective antigen (UL25); also shown are images for the mock-vaccinated control and the dl5-29 positive control. The indicated P values show statistical significance between the HSV-2-vaccinated and mock-vaccinated control groups. *, P < 0.05 (considered significant).