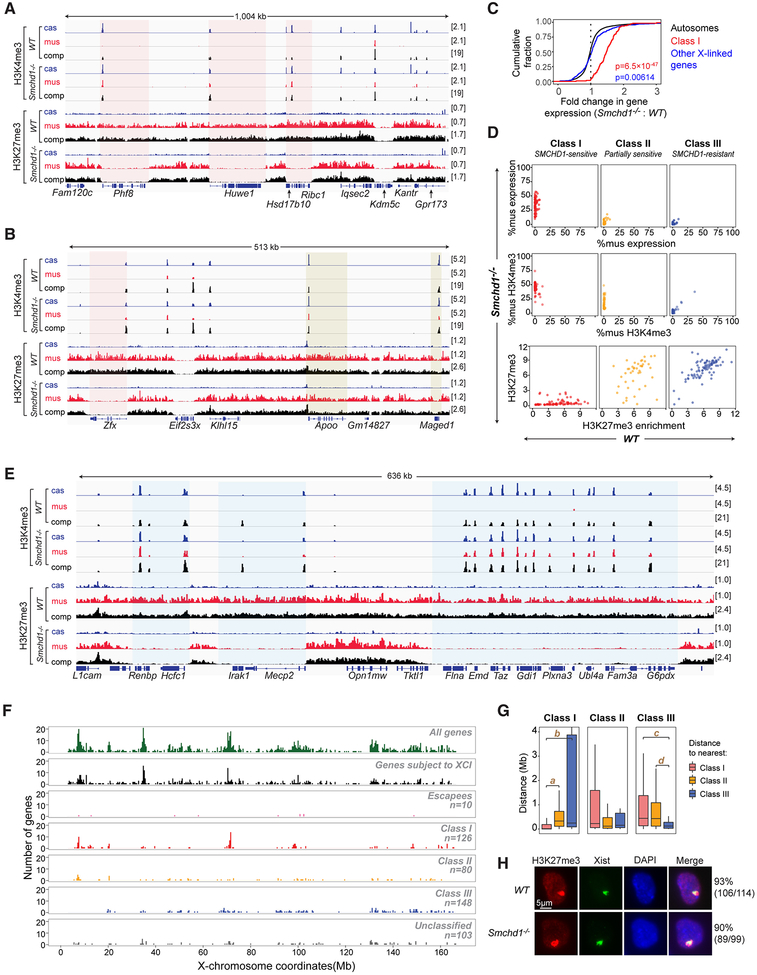
Figure 2. Segmental erosion of H3K27me3 domains reveals SMCHD1’s role in spreading heterochromatin.
(A) H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 profiles for representative Class I genes (red-shaded area) and an escapee (Kdm5c). cas, mus, comp as defined in Fig 1.
(B) H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 profiles for representative Class II genes (yellow-shaded area). Zfx, a Class I gene. Eif2s3x, an escapee.
(C) CDPs of fold-changes in gene expression between Smchd1-/- and WT cells for autosomal genes (black), Class I genes (red), and all other X-linked genes (black). P-values by Wilcox test (unpaired, one-sided). Between Class I versus autosomal genes (red), and all other X-linked genes versus autosomal genes (blue).
(D) For each of three gene classes, comparison of allelic skewing in expression (top), allelic skewing of H3K4me3 peaks at promoters (middle), and H3K27me3 enrichment in gene bodies (bottom) between Smchd1-/- (y-axes) versus WT (x-axes) cells.
(E) Failure of H3K27me3 spreading covering intergenic regions and gene bodies of Class I genes (blue-shaded area).
(F) Chromosomal locations of various categories of X-linked genes. We segmented the X into 400-kb bins and plotted the number of genes for each category.
(G) Nearest neighbor analysis: Box plots showing distance relationships of Class I, II, and III genes to each other. E.g., the left panel shows the distribution of distances from a Class I gene to the nearest Class I (red), Class II (yellow), or Class III (blue) gene. NS: not significant (P>0.05). a, P=3.3×10−14. b, P=6.3×10−16. c, P=5.0×10−11. d, P=9.9×10−11(Wilcox test).
(H) Immuno-RNA-FISH for H3K27me3 and Xist RNA on WT and Smchd1-/- NPCs. Number of cells with an Xist cloud and a co-localizing H3K27me3 focus shown.