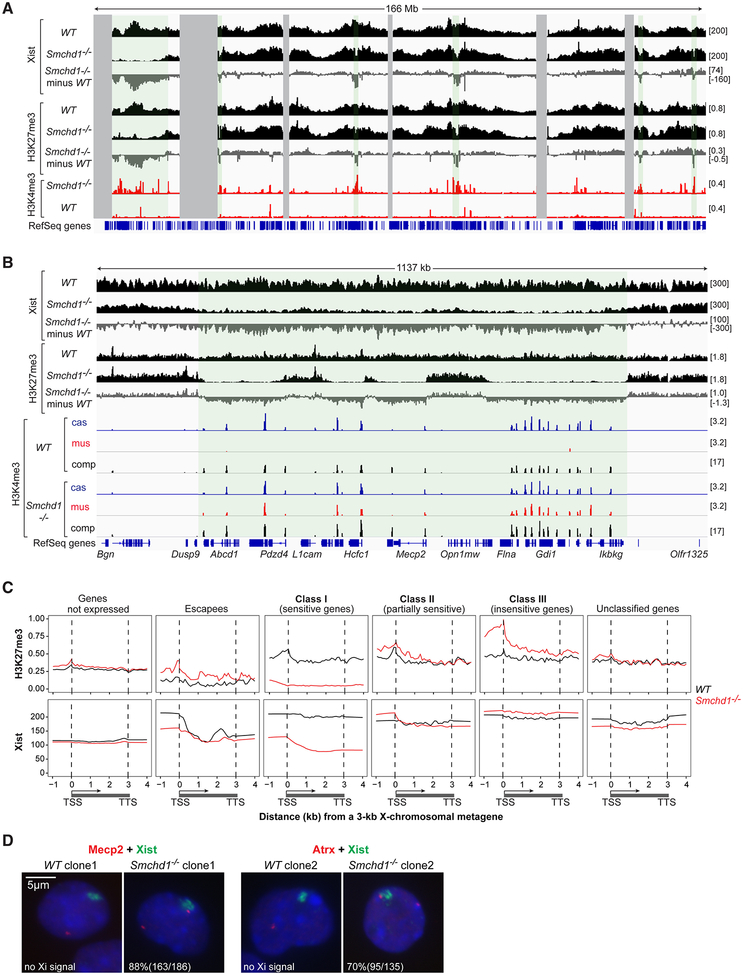
Figure 3. SMCHD1 deficiency results in regional Xist spreading defects.
(A) Xist binding patterns (CHART-seq, comp), H3K27me3 enrichment (ChIP-seq, comp), and H3K4me3 enrichment (ChIP-seq, mus) across X chromosome. Enrichment difference determined by subtracting WT from Smchd1-/-. Green-shaded area, Xist-depleted regions. Gray-shaded area, unmappable regions.
(B) Xist binding patterns, H3K27me3 and H3K4me3 enrichment across one representative Xist-depleted domain.
(C) Metagene analysis of H3K27me3 and Xist enrichment in WT versus Smchd1-/- NPCs. Different X-linked gene categories are shown. The Xist locus was excluded as an escapee. TSS, transcription start site. TTS, transcription termination site. Gene bodies are “squished” between distances from 1–3 kb. Upstream and downstream regions are in absolute distance (kb).
(D) Two color RNA FISH for Xist and Mecp2 (left) or Atrx (right) in WT versus Smchd1-/- cells. %nuclei shown with nascent Mecp2 or Atrx signal outside or overlapping the edge of Xist cloud. In WT cells, 85% (159/186) of nuclei show monoallelic Mecp2 and 96% (129/134) show monoallelic Atrx. In Smchd1-/- cells, 73% of Mecp2 is biallelic (186/255), and 88% of the Xi allele is outside of Xist cloud; for Atrx, 80% is biallelic (135/168), and 70% of the Xi allele is outside of Xist cloud.