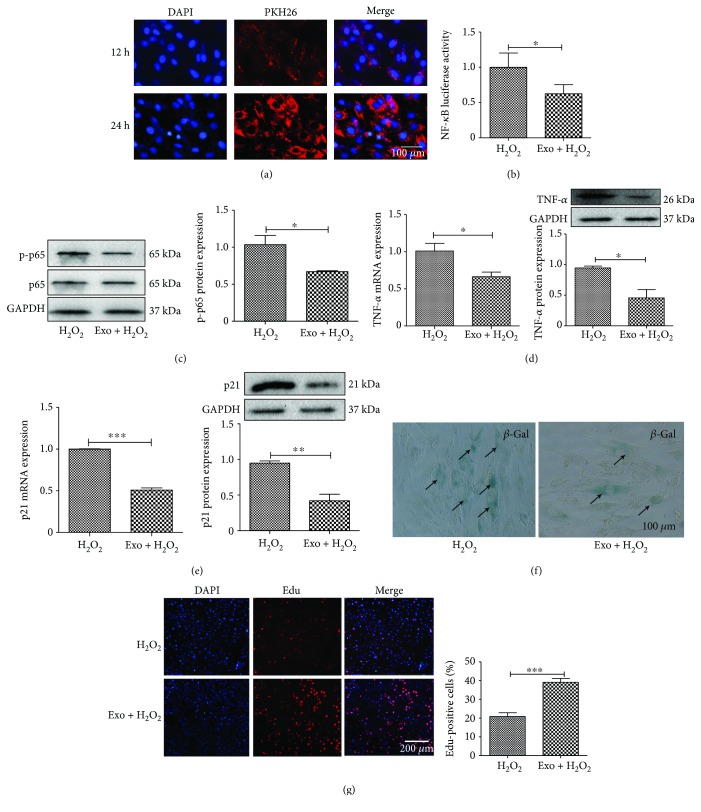
Figure 5.
EXO inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway. (a) H9C2 was incubated with PKH26-labeled exosome (EXO), and the uptake of EXO was observed under a fluorescent microscope. (b) Luciferase assay for NF-κB activation. Cardiomyocytes were transfected with NF-κB-luc and RL-TK plasmids by Lip 2000 for 24 h, and EXO (200 μg/mL) was added to the cells and incubated for another 24 h. The cells were then treated with H2O2 for 6 h. (c) Western blot analysis of p-p65 expression. (d) RT-PCR and Western blot analysis of TNF-α expression. (e) RT-PCR and Western blot analysis of p21 expression. (f) Immunohistochemistry staining of β-gal in cardiomyocytes treated with EXO. (g) Edu staining for cell proliferation treated with EXO. N = 4/group∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001.