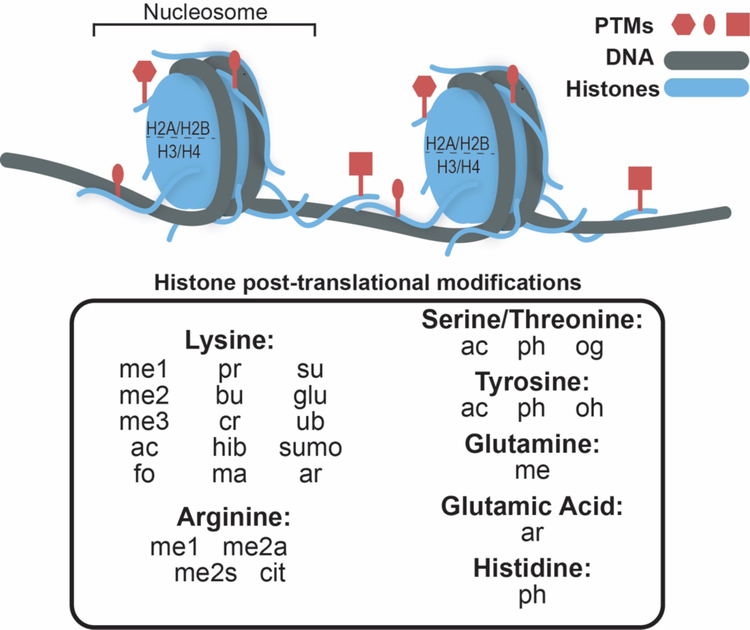
Figure 1. Histone post-translation modification.
The nucleosome, the basic subunit of chromatin, consists of an octamer of histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 (blue) wrapped by ~147 base pairs of DNA (gray). Histone post-translational modifications (red) are enriched in the tail domains. A list of identified histone modifications is shown below. Abbreviations are: monomethylation (me1), di-methylation (me2), tri-methylation (me3), acetylation (ac), formylation (fo), propionylation (pr), butyrylation (bu), crotonylation (cr), 2-hydroxylisobutyrylation (hib), malonylation (ma), succinylation (su), glutarylation (glu), ubiquitylation (ub), sumoylation (sumo), ADP ribosylation (ar), symmetric di-methylation (me2s), asymmetric di-methylation (me2a), citrullination (cit), phosphorylation (ph) and O-GlcNacylation (og), and hydroxylation (oh).