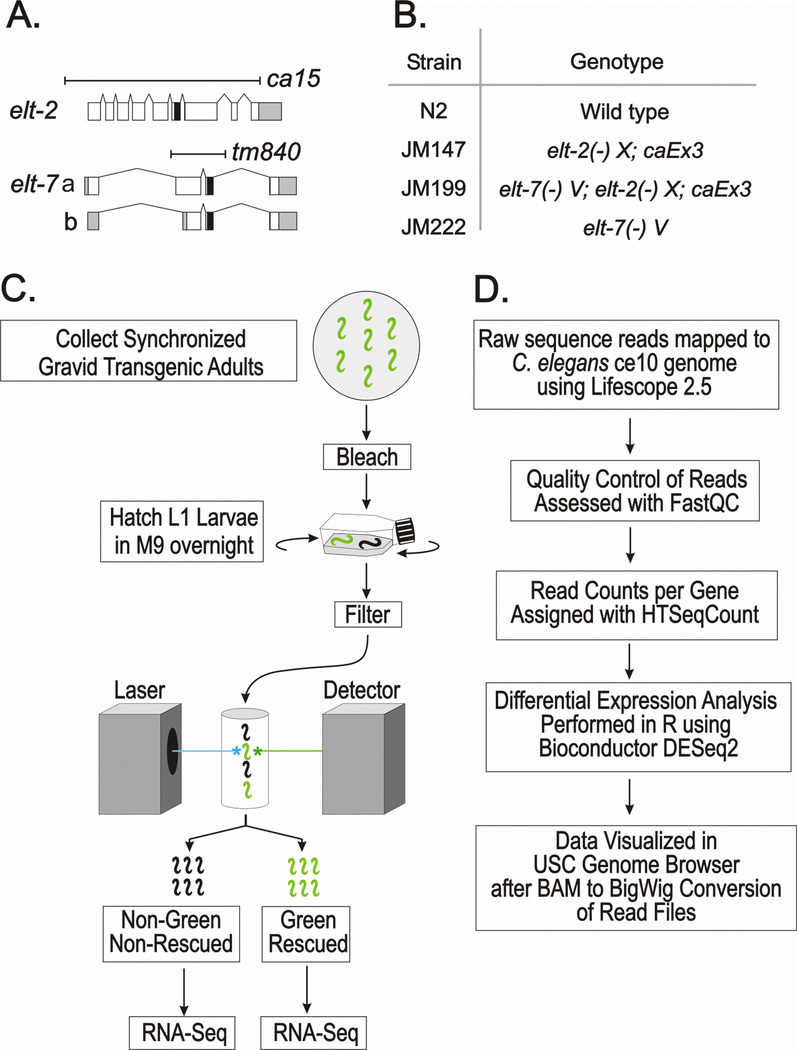
Fig. 1. Overall experimental design: Genotypes, sorting protocol and outline of bioinformatic methods.
A. Diagram of the elt-2 and elt-7 genes; white, gray and black boxes represent coding regions, untranslated regions and the zinc finger DNA binding domains, respectively. Both deletion alleles remove the DNA binding domain and are presumed null mutations.
B. Genotypes of the four strains used in the present analysis. elt-2(−) refers to allele ca15; elt-7(−) refers to allele tm840. In the two strains JM147 and JM199, the lethality associated with the elt-2(−) mutation is rescued by the same multicopy extra-chromosomal array caEx3[elt-2(+); rol-6(su1006); sur-5::GFP], which is lost in ~50% of the progeny of a transgenic mother.
C. Summary of sample preparations prior to RNA-Seq. Arrested L1 larvae from all four strains (N2, JM147, JM199 and JM222) were passed through the COPAS Biosorter in exact parallel.
D. Summary of major steps in the bioinformatic analysis.