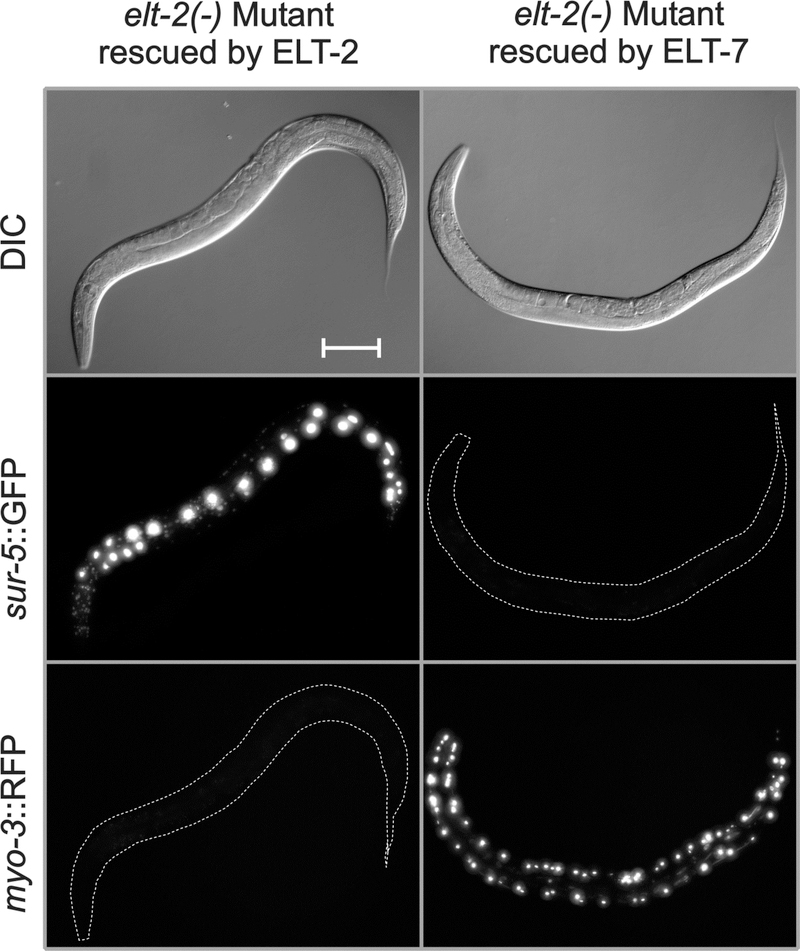
Fig. 5. ELT-7 expressed under control of the elt-2 promoter can rescue the elt-2(−) lethal arrest phenotype.
The three panels on the left are images of the starting strain JM147 in which the elt-2(−) mutation is rescued by an extrachromosomal transgenic array containing the genomic elt-2(+) gene and sur-5::GFP. As shown in the three panels on the right, the elt-2(+) rescuing array in JM147 can be replaced by a second extrachromosomal transgenic array containing the elt-2 promoter driving expression of an elt-7 cDNA as well as a myo-3::RFP construct expressed in bodywall muscle. Animals shown are one day past L4 stage. Images, from top to bottom, are Differential Interference Contrast (DIC), maximum point projection of a GFP stack, and maximum point projection of an RFP stack. Microscopic and image analysis parameters are identical between the two animals, except that the GFP exposure for the ELT-7 rescued strain was 4-fold higher than for the starting strain, in order to ensure that even faint GFP expression could have been detected. Scale bar = 100 microns.