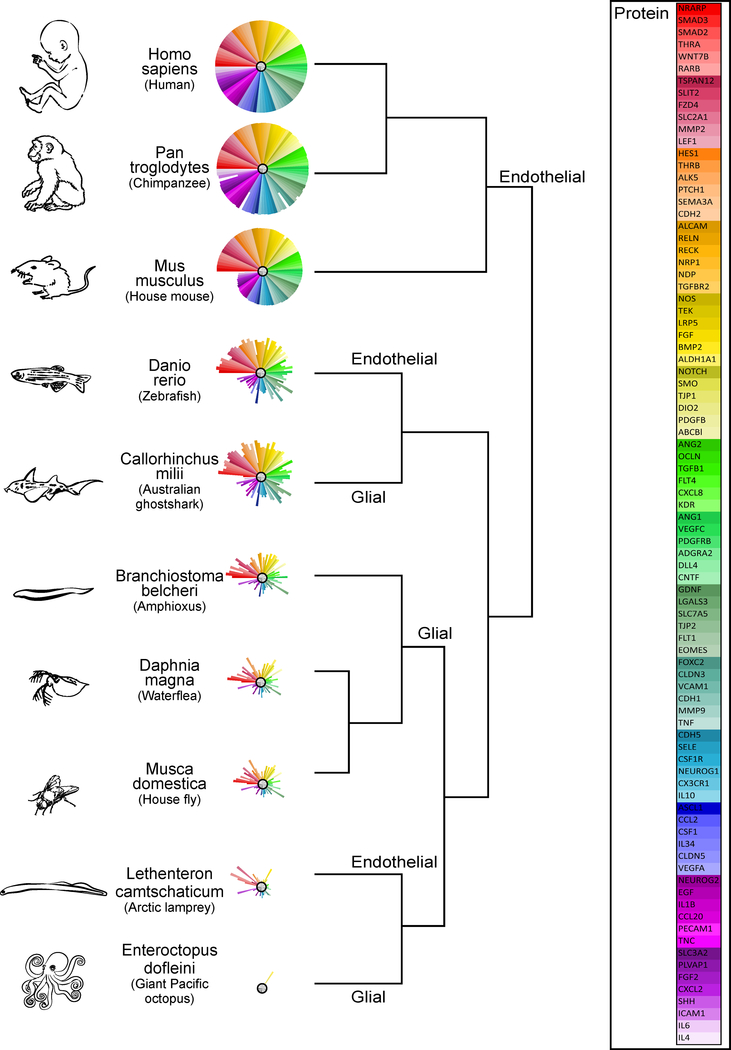
Figure 2: Phylogeny of the BBB.
Primary amino acid sequence similarity for 86 proteins implicated in BBB development (see figure 4) was determined for species representing classes that appear at different times throughout evolutionary history: (Mammalia: Homo sapiens, Pan troglodytes, Mus musculus; Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish): Danio rerio; Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish): Callorhinchus milii; Leptocardii (earliest vertebrates): Branchiostoma belcheri; Branchiopoda (crustaceans): Daphnia magna; Insecta: Musca domestica; Hyperoartia (invertebrate chordate): Lethenteron camtschaticum; Cephalopoda: Eteroctopus dofleini). Comparisons to the human protein (100%) were made by an amino acid sequence query using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool for proteins (BLASTp) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) protein database using SeqAPASS v2.0 software (https://seqapass.epa.gov/seqapass) (LaLone et al., 2016), which facilitates consistent comparisons of amino acid sequence similarity across multiple species. For proteins with multiple isoforms, SeqAPASS best practices were used to select the most representative NCBI protein accession number for the BLAST; and full sequence lengths (rather than functional domains) were used. A beta testing version of ToxPi software v2.0 provided by David Reif (NCSU) was used to produce the sequence similarity ToxPis using the ‘single’ clustering algorithm (Reif et al., 2010). For each protein, the % similarity to the human protein (100%) is represented by the length of pie slice (i.e., shorter pie slices represent lower similarity; or absence of a slice indicates no sequence similarity). Slices are arranged from highest to lowest % similarity in the mouse compared to humans (i.e., red slices have the highest similarity and light purple slices represent the lowest similarity). The type of BBB (glial or endothelial) is indicated on the dendrogram at the node representing a common ancestor with the same type of BBB. The symbols listed in the ‘protein’ key correspond to standard NCBI gene names. NCBI protein database accessed between 6/27/17 and 7/27/17.