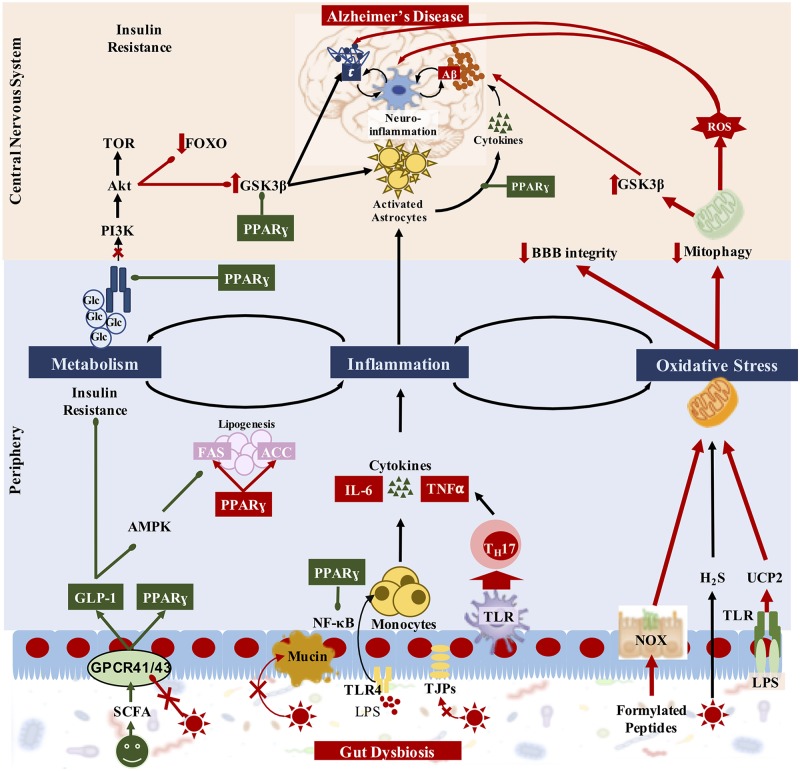
Fig 7. Proposed mechanisms of PPARγ interference with gut-brain-axis communication in the context of Alzheimer’s disease.
Metabolism, inflammation and oxidative stress are three physiological states whose integrated pathology forms the main stochastic risk factors of Alzheimer’s disease. The gut microbiota and its associated metabolites influence each of these axes through several mechanisms as depicted here. Abbreviations: GPR—G-protein receptor; SCFA—short chain fatty acids; GLP-1—glucagon like protein; PPAR—peroxisome proliferator activated receptor; TLR—toll like receptor; TJP—tight junction protein; IL-6; interleukin-6; TNF—tumor necrosis factor; NOX—NADPH oxidase; H2S—hydrogen sulfite; UCP2—uncoupled protein 2; LPS—lipopolysaccharide; GSK3β—glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; PI3K—phosphoinositide-3 kinase; FOXO—Forkhead box protein O; Akt—protein kinase B; ROS—reactive oxygen species; BBB—blood brain barrier.