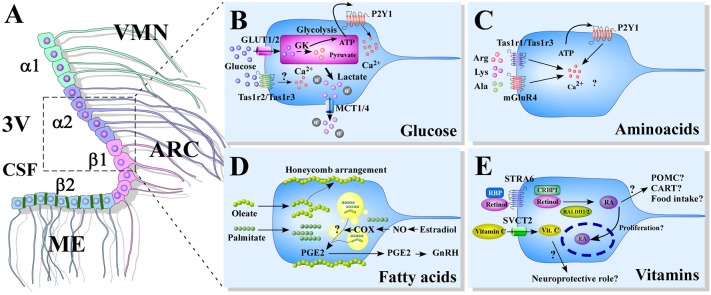
Figure 1.
Models of nutrient sensing mediated by tanycytes. (A) A schematic representation of the distribution of tanycytes over the wall of the third ventricle (3V). The α1-tanycytes in light green (α1) have long projections that make contact with the neurons of the VMN. α2-tancycytes in purple (α2), have projections to the ARC. β1-tanycytes in pink (β1), make projections to the ARC. Finally, in the floor of the 3V, β2-tanycytes in light blue (β2), are joined by tight junctions forming part of the median eminence (ME)-cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) barrier, and their projections make contact with the ME. (B–E) Scheme based on proposed glucose (B), aminoacids (C), fatty acids (D), and vitamins (E) sensing mechanism mediated by tanycytes. 3V: third ventricle; CSF, cerebral spinal fluid; ME, median eminenece; ARC, arcuate nucleus; VMN, ventromedial nucleus; GK, glucokinase; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; GnRH, Gonadotropin-release hormone; RBP, Retinol binding protein; STRA6, RBP receptor; CRBP1, cellular retinol-binding protein; RALDH, retinaldehyde dehydrogenase; RA, retinoic acid; POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin; CART, cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript; SVCT2, sodium vitamin C co-transporter 2.