Figure 1.
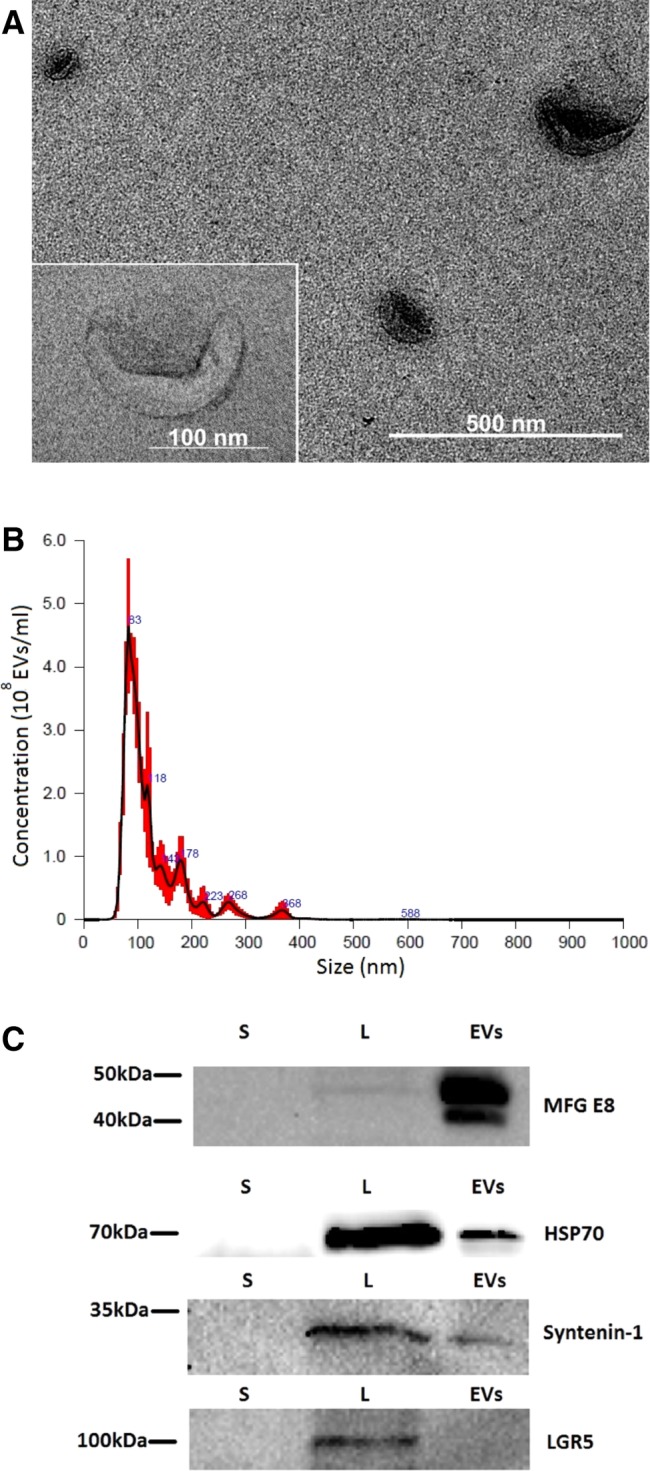
Characterization of extracellular vesicles (EVs) isolated from stem cells from the dental pulp of human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHEDs). (A): Transmission electron microscopy of EVs isolated from SHEDs (×30,000 magnification). A magnified image of EV is shown on the left panel (×120,000 magnification). (B): Determination of the concentration and particle size of EVs derived from SHEDs. Nanoparticle tracking analysis was performed with NanoSight LM10 instrument (Malvern Panalytical). Size distribution of the EVs was around 100 nm. (C): Samples from supernatants (S), cell lysates (L), and EV fractions (EVs) were subjected to electrophoresis, blotted and the membrane was probed with antibodies against EV markers (HSP70, MFG‐E8, syntenin‐1), or LGR5 as a negative control. Bands were visualized by incubation with appropriate horseradish peroxidase‐conjugated secondary antibodies and chemiluminescence substrate.
