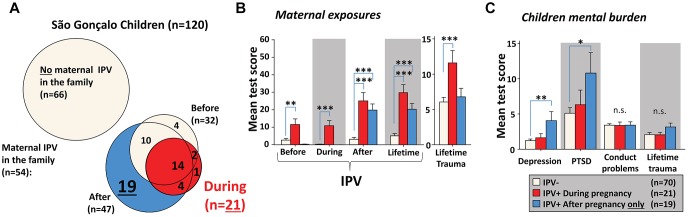
FIGURE 1.
Missing psychiatric problems in São Gonçalo children following prenatal IPV. Most mothers experiencing pregnancy IPV were also exposed to IPV before conception or after giving birth (A). A substantial number of mothers experienced IPV only after birth. Despite similar maternal IPV exposures after birth in both prenatally and only postnatally exposed children, and even higher lifetime trauma exposures in mothers experiencing IPV during pregnancy (B), only children living in families with mothers exposed to IPV only postnatally expressed more depression and PTSD symptoms (C). Results in (B,C) originates from Bonferroni corrected post hoc tests, using general linear models with age, sex, pregnancy/prenatal trauma and CDV scores as covariates. Error bars indicates ±SEM. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05.