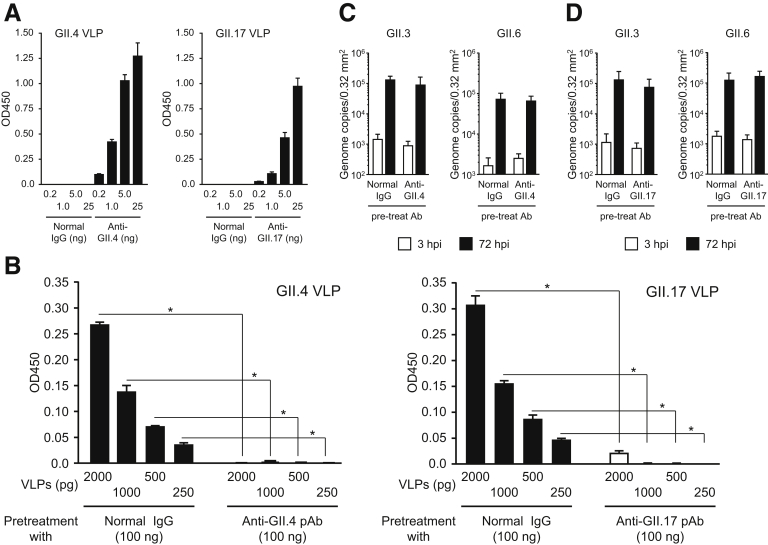
Supplementary Figure 3.
Binding of GII.4 and GII.17 VLPs to histo-blood group antigens is prevented by pre-treatment with each anti-VLP polyclonal antibody (pAb). (A) Homotypic titer of anti-GII.4 and GII.17 pAbs were quantified by enzyme-linked immnosorbent assay. Data are means ± SD from 1 experiment representative of 2 independent experiments. (B) Blocking activity of anti-GII.4 and anti-GII.17 toward VLP–histo-blood group antigen binding was measured by ELISA. Data are mean ± SD from 1 experiment representative of 3 independent experiments. *P < .05. GII.3 and GII.6 HuNoVs (2 × 106 genome equivalents) were incubated with 100 ng of (C) anti-GII.4 or (D) anti-GII.17 antibody, or with normal rabbit IgG, for 1.5 hours. Monolayered human iPSC–derived IECs were inoculated with each treated HuNoV. Viral genome RNA was extracted from both supernatants, and the genome equivalents were quantified by reverse transcriptase qPCR. Samples at 3 hpi were used as references. Each value is representative of 3 independent experiments and is shown as the mean ± SD from 4 to 6 wells of supernatants of each culture group.