Figure 4.
Crystal Structure of FIP200 CTR
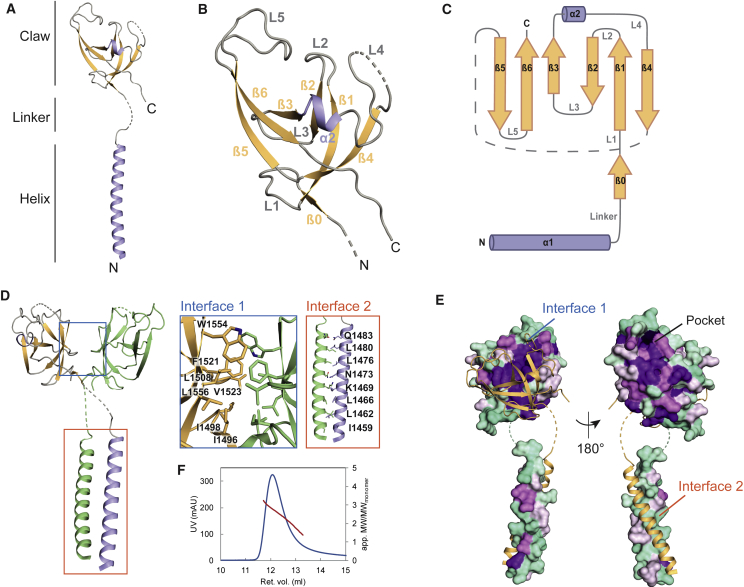
(A) Crystal structure of the FIP200 CTR monomer. The molecule comprises a helix, a linker, and a globular Claw domain. The structure is colored according to its secondary structure elements (helix, purple; β strands, orange; loops, gray).
(B) Close-up of the Claw domain. The fold resembles a Claw with the β sheet being the palm of the Claw and loops L2, L4, and L5 flexed fingers. Same view and coloring used in (A).
(C) Topology plot of monomeric FIP200 CTR. α helices are shown as purple cylinders and β strands as orange arrows.
(D) Dimerization of FIP200 CTR. The homodimer is formed via two interfaces: interface 1 (blue box) and interface 2 (red box). Monomers are colored in orange and green. Interface residues are shown as sticks and labeled for only one monomer.
(E) Surface conservation plot of the FIP200 CTR monomer based on the sequence alignment of 11 different species (Figure S5B). Conserved residues are colored in purple and non-conserved residues in cyan. The second monomer is shown in cartoon representation.
(F) Analytical size-exclusion chromatography coupled to right-angle light scattering. Absorption at 280 nm (blue) and oligomeric state (as apparent molecular weight, divided by molecular weight of the monomer) (red) are plotted against the retention volume (mL).
See also Figures S4 and S5.