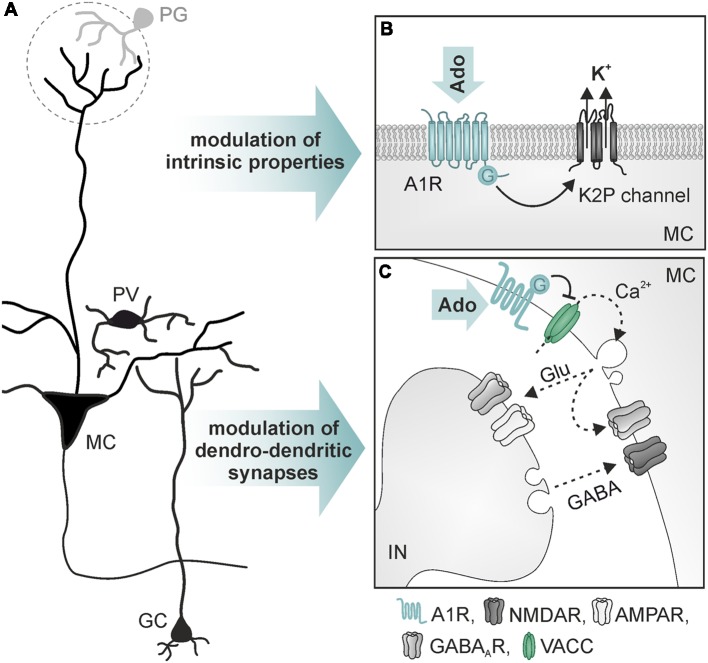
Figure 4.
Mechanisms of action of adenosine in mitral cells. (A) Simplified neuronal network in the olfactory bulb. (B) Opening of two-pore domain potassium channels (K2P) by activation of A1 receptors leads to hyperpolarization of mitral cells (MC). (C) A1 receptor-mediated reduction of Ca2+ influx into presynaptic sites of MC reduces dendro-dendritic inhibition at reciprocal synapses between MC and interneurons (IN; GC and parvalbumin-positive interneurons). Abbr.: Ado, adenosine; Glu, glutamate; GC, granule cells; PG, periglomerular interneuron; PV, parvalbumin-positive interneuron; VACC, voltage-activated calcium channel. Illustration by SciGraphics.