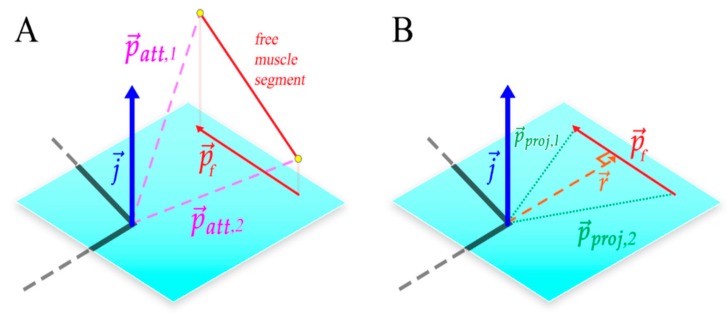
Figure 4.
Calculating the muscle moment arm, r. (A) The plane of interest and its coordinate system is defined by the joint center and the joint axis representing flexion/extension (blue). Joint axes are defined using the same convention as Johnson et al. [17] and Charles et al. [18]. Orthogonal joint axes represent abduction/adduction, and inversion/eversion. (B) The free muscle segment that connects the adjacent bone segments (monoarticular muscles) or to the bone segment after the next (biarticular muscles) is projected onto the plane of interest. This projected free segment is called . The muscle moment arm r, is calculated from the joint axis and .