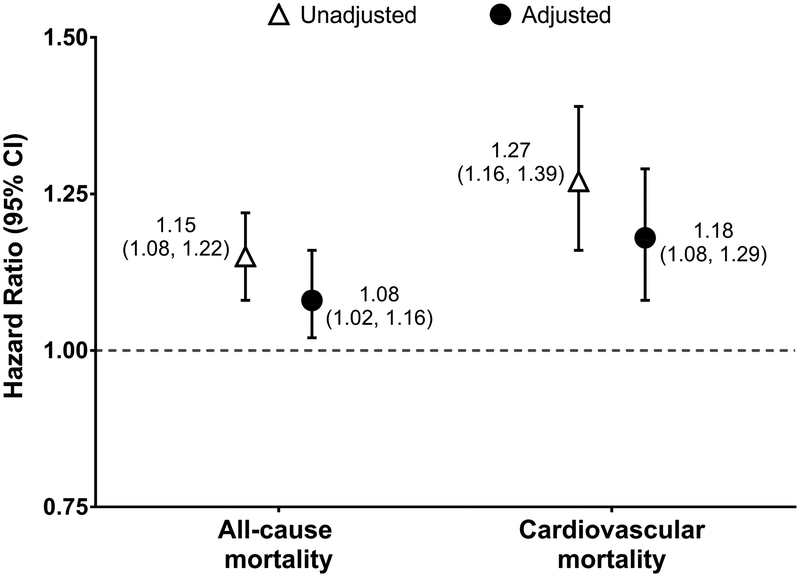
Figure 3. Association between carvedilol versus metoprolol initiation and 1-year mortality: intent-to-treat analysis.
An intent-to-treat design was employed in all analyses. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the association between carvedilol (versus metoprolol) initiation and 1-year all-cause mortality. Fine and Gray proportional subdistribution hazards models were used to estimate the association between carvedilol (versus metoprolol) initiation and 1-year cardiovascular mortality. In cardiovascular mortality analyses, non-cardiovascular death was treated as a competing risk. Inverse probability of treatment weighting was used in adjusted analyses to control for all the baseline covariates listed in Table 1.
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; ref., referent