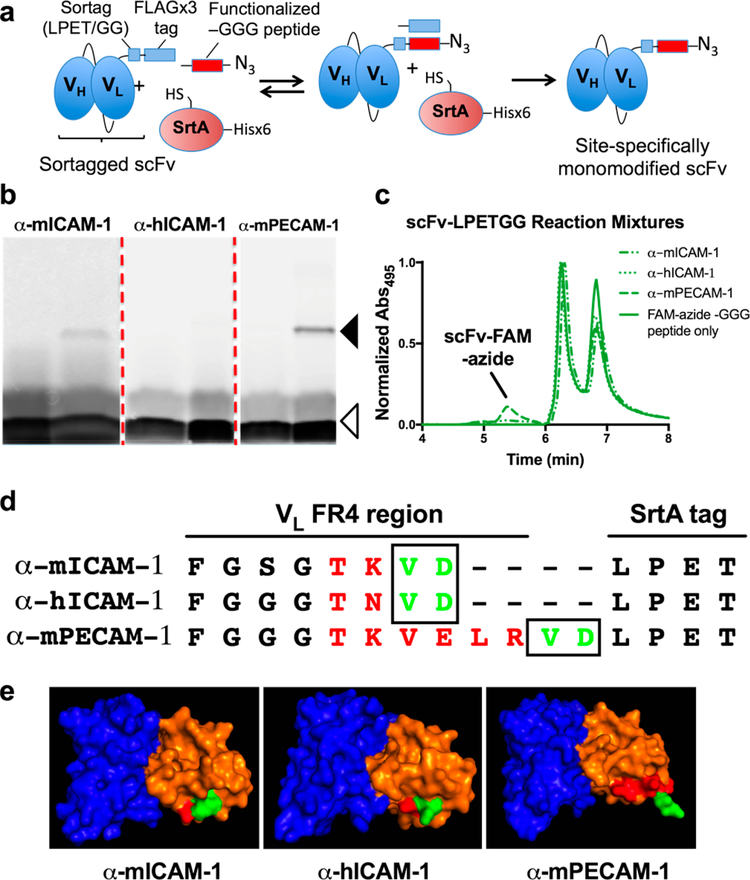
Figure 1.
Sortase modification of scFv-LPETGG proteins. (a) Schematic of the reversible sortase (SrtA) reaction, in which the transpeptidase enzyme removes the C-terminal FLAGx3 tag and appends a fluorescently labeled, azide-modified peptide. (b) SDS-PAGE analysis of reaction mixtures shows clear difference in the reaction efficiency of the three clones. Solid arrowhead indicates size of modified scFv–LPETGG, whereas open arrowhead indicates free TAMRA–azide–GGG peptide (runs as two bands on the gel). (c) HPLC analysis of scFv–LPETGG reaction mixtures confirms difference in α-mPECAM-1 scFv reaction efficiency vs the other two clones. Note that free FAM–azide–GGG peptide elutes in two peaks on SEC. (d) Primary structure of each protein at the scFv C-terminus, showing distinct positioning of amino acids VD (encoded by the sequence of restriction enzyme site SalI). (e) Predictive 3-D modeling of each scFv–LPETGG clone, showing the putative positions of VH (blue) and VL (orange), with the C-terminal amino acids of framework region 4 (FR4) shown in red and amino acids VD shown in green.