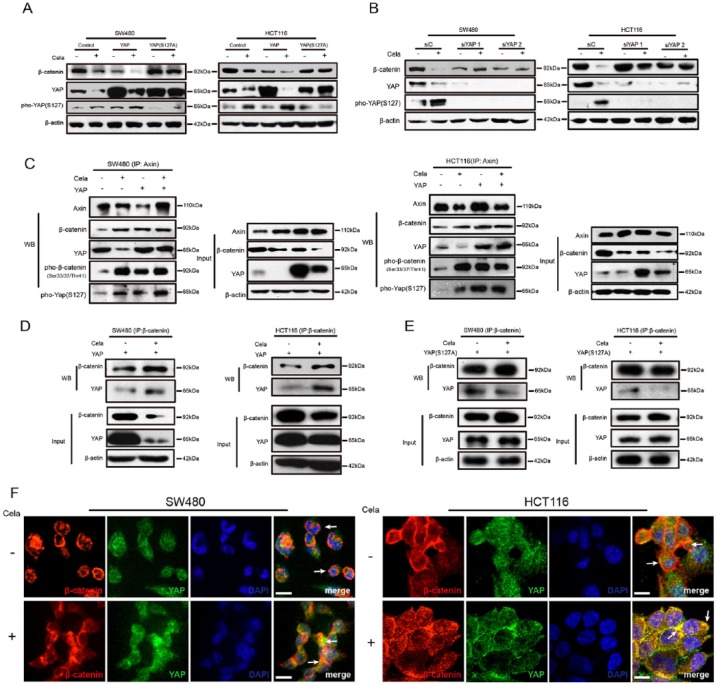
Figure 3.
Yes-associated protein (YAP) was involved in Celastrol-induced β-catenin degradation.
(A) SW480 and HCT116 cells were transfected with control plasmid or plasmids expressing wide-type YAP or mutant YAPS127A for 24 h, and treated with or without Celastrol (0.75 μM) for another 24 h, respectively. β-catenin, YAP, and pho-YAP (S127) were detected and β-actin was used as a loading control.
(B) SW480 and HCT116 cells were transfected with scramble or YAP-specific siRNA for 24 h, and treated with or without Celastrol (0.75 μM) for another 24 h, respectively. β-catenin, YAP, and pho-YAP (S127) were detected. β-actin was used as a loading control.
(C) SW480 and HCT116 cells were transfected with control plasmid or YAP-expressing plasmid for 24 h, and treated with or without Celastrol (0.75 μM) for another 24 h, respectively. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with Axin antibody, followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against Axin, β-catenin, YAP, pho-β-catenin (Ser33/37/Thr41), and pho-YAP (S127) as indicated. Total lysates were used as input control.
(D), (E) SW480 and HCT116 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing wildtype YAP or mutant YAPS127A for 24 h, and treated with or without Celastrol (0.75 μM) for another 24 h, respectively. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with β-catenin antibody, followed by immunoblotting with antibodies against β-catenin and YAP. Total lysates were used as input control.
(F) Immunofluorescence of β-catenin and YAP in SW480 and HCT116 cells, treated with or without Celastrol (0.75 μM) for 24 h. Scale bar: 5 μm.