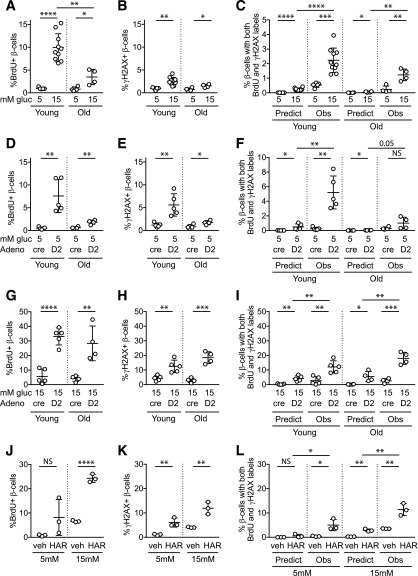
Figure 2.
Proliferative stimuli, especially in combination, increase BrdU-γH2AX colocalization frequency in mouse β-cells. Dispersed young (10- to 12-week-old) and old (50- to 60-week-old) mouse islet cells were cultured for 72 h in the indicated conditions, with BrdU added for the final 24 h. A 15 mmol/L glucose concentration markedly increased BrdU incorporation (A), especially in young islets, and modestly increased γH2AX labeling (B) and BrdU-γH2AX colabeling (C). Ad-cyclin D2 in 5 mmol/L glucose increased BrdU (D), γH2AX (E), and colabeled cells (F). Combined treatment with 15 mmol/L glucose and Ad-cyclin D2 markedly increased BrdU (G), γH2AX (H), and colabeled cells (I). Exposure to a different β-cell mitogen, harmine, also increased BrdU (J), γH2AX (K), and colabeled cells (L). Note the variable y-axis scale in A–L. C, F, I, and L: in all cases, the observed fraction of β-cells colabeled for both BrdU and γH2AX was greater than that predicted if colabeling occurred due to chance. Ad-cre was used as a control for Ad-cyclin D2. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Adeno, adenovirus; gluc, glucose; HAR, harmine; Obs, observed; Predict, predicted; veh, vehicle.