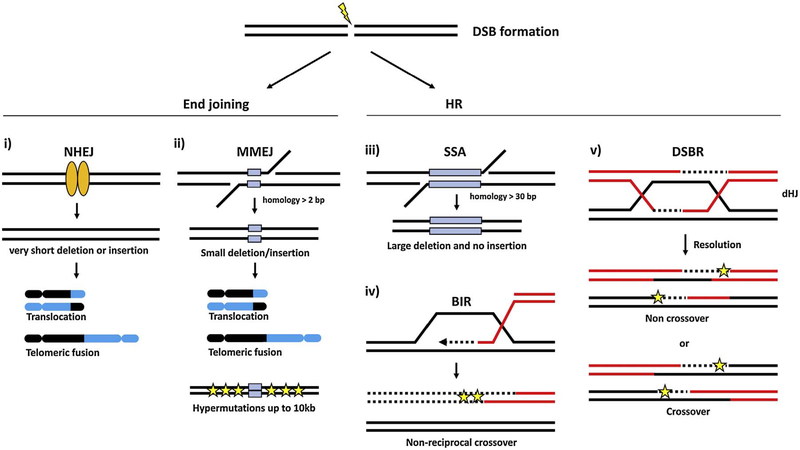
Fig. 2.
Genomic instability caused by DNA DSB repair mechanisms. C-NHEJ (i) generates small sequence deletions/insertions at breakpoint junctions. MMEJ (ii) induces deletions and insertions at the breakpoint junctions and hypermutagenesis at the flanking DNA sequence up to several kilobases from the break. Both C-NHEJ and MMEJ could trigger chromosomal translocations and telomeric fusions. SSA (iii) also induces large deletions but not insertions at repair junctions. In BIR (iv) and gene conversion (v), low fidelity DNA synthesis produces mutagenesis at the flanking DNA sequence and could induce chromosomal translocations if recombination involves non-allelic template and/or crossover formation. Blue boxes represent homologies and the stars represent mutations. The dotted lines are newly synthesized DNA. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)