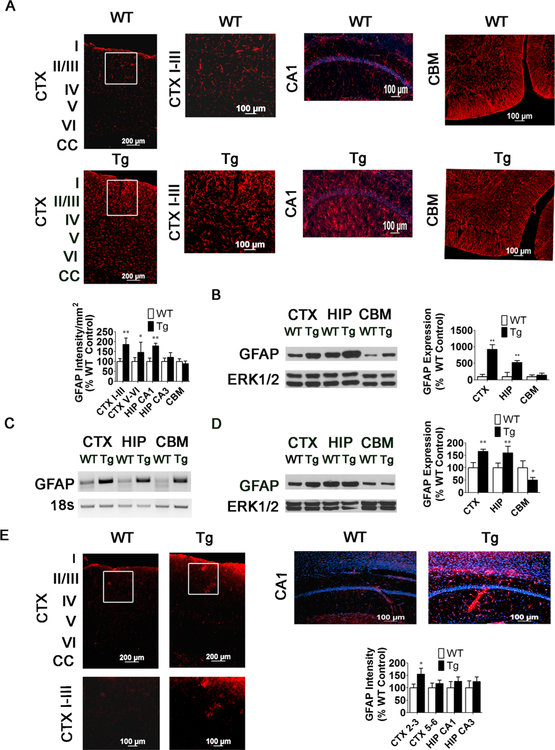
Fig. 7.
Increase in GFAP expression in MeCP2-Tg brain precedes neuronal loss but occurs in the same regions that subsequently display neuronal loss. a GFAP staining and measurement of staining intensity in the CTX, HIP, and CBM of 15-week-old WT and MeCP2-Tg mice (n = 9). CTX shows low- magnification image (left panels) and high-magnification images (right panels). The white box in low-magnification image denotes location of high-magnification image. b Western Blot and quantification showing expression of GFAP in CTX, HIP, and CBM of 15-week-old WT and MeCP2-Tg mice (n = 7). c GFAP RT-PCR in the CTX, HIP, and CBM of 15-week-old Tg mice. Eighteen seconds was used to normalize cDNA. d Western Blot and quantification showing expression of GFAP in the CTX, HIP, and CBM of 10-week-old WT and MeCP2-Tg mice (n = 5). ERK1/2 serves as a loading control. e GFAP staining and measurement of staining intensity in the CTX, HIP, and CBM of 15-week-old WT and MECP2-Tg mice (n = 6). For CTX, upper panels are lower-magnification images and lower panels are higher-magnification images. The white box in the lower- magnification images denotes locations of the higher-magnification images