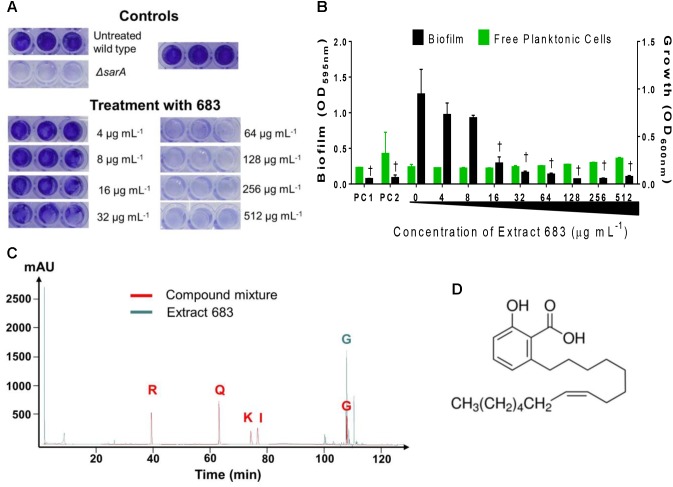
FIGURE 5.
Biofilm inhibition assay on S. aureus UAMS-1 and identification of five Ginkgo standard compounds for the most active Ginkgo extract (no. 683). (A) Images of crystal violet stained biofilm in 96-well plates. USA 200 isolate UAMS-1 and its isogenic sarA mutant (UAMS-929) were used in the biofilm assay. (B) The optical density (OD595 nm) of the crystal violet eluent is plotted with the OD600 nm for planktonic cells, measured by transfer of the well supernatants to a new 96-well plate. Two different positive controls (PC) are represented in the figure: PC1 = 220D-F2 extract; PC2 = ΔsarA mutant as previously described (Quave et al., 2012). Statistical significance in comparison to the vehicle treated wild type control is denoted as †P < 0.001. (C) HPLC chromatograms at 245 nm of Ginkgo standard compounds (i.e., quercetin 0.4 mg/mL, isorhamnetin 0.2 mg/mL, kaempferol 0.4 mg/mL, rutin 0.4 mg/mL, ginkgolic acid C15:1 0.4 mg/mL) and Ginkgo extract no. 683 (10 mg/mL) are shown in red and green line, respectively. (D) Chemical structure of ginkgolic acid C15:1.