Fig. 2.
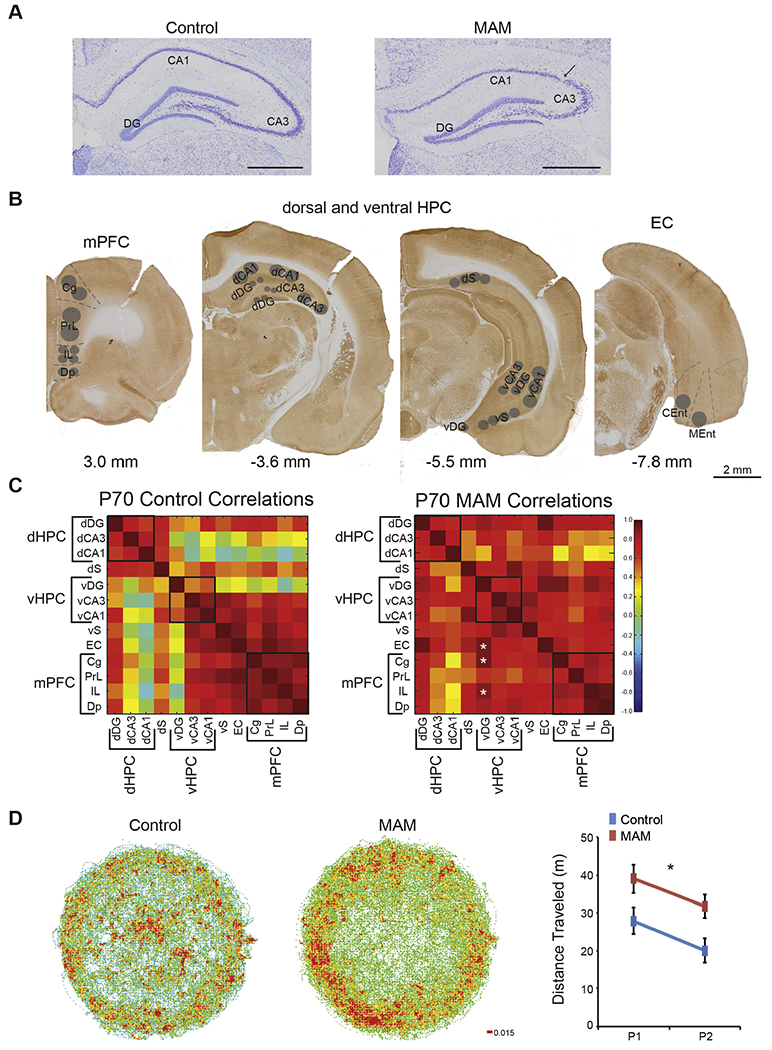
MAM rats are hyperactive and have altered functional connectivity between hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. (A) Nissl stained tissues show that MAM rats have a thinned and disrupted pyramidal cell layer in the hippocampus. (B) Cytochrome oxidase activity was measured in the prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and entorhinal cortex. Subregions are as follows: Cg = cingulate cortex, PrL = prelimbic cortex, IL = infralimbic cortex, Dp = dorsal peduncular nucleus, dDG = dorsal dentate gyrus, dCA3 = dorsal Cornu Ammonis 3 of the hippocampus, dCA1 = dorsal Cornu Ammonis 1 of the hippocampus, dS = dorsal subiculum, vDG = ventral dentate gyrus, vCA3 = ventral Cornu Ammonis 3 of the hippocampus, vCA1 = ventral Cornu Ammonis 1 of the hippocampus, vS = ventral subiculum, EC = entorhinal cortex, CEnt = caudal entorhinal cortex, and MEnt = medial entorhinal cortex. (C) MAM rats have altered functional connectivity between the ventral dentate gyrus and the prefrontal cortex as well as between the ventral dentate gyrus and the entorhinal cortex. Black boxes represent groupings of subregions into functional domains: dHPC = dorsal hippocampus, vHPC = ventral hippocampus, and mPFC = medial prefrontal cortex. All other abbreviations are the same as in B. Values are Pearson Product Correlations. MAM, n = 8. Control, n = 8. * Group differences, p < 0.05. (D) MAM rats display spontaneous hyperactivity in the open field and habituate to a new environment. (Group: F1,14 = 7.15, p = 0.02; Trial: F1,14 = 5.76, p = 0.03; Interaction: F1,14 = 0.00, p = 0.97). P1 and P2 are pretraining trial 1 and 2 respectively. Values for the locomotor activity are average ± SEM. MAM, n = 8. Control n = 8. * p < 0.05.
