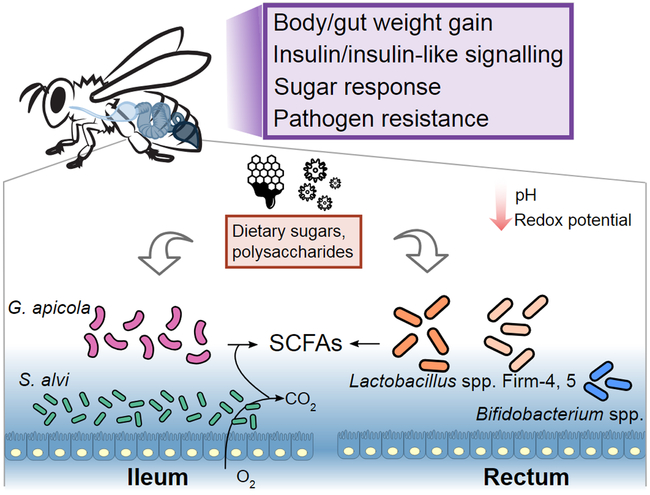
Figure 3.
Summary of the effects of the honey bee gut microbiota on host and the gut microbial metabolism. The dominant members in the ileum and rectum ferment sugars and polysaccharides from the host diet (honey and pollen) to SCFAs. Oxygen consumption by the species S. alvi, which forms a layer attached to the inner gut wall, maintains an anoxic gut environment. The presence of gut bacteria can also reduce the gut pH and redox potential. Moreover, gut bacteria have various effects on the weight gains, insulin signaling, behaviors, and pathogen resistance of the hosts.