1.
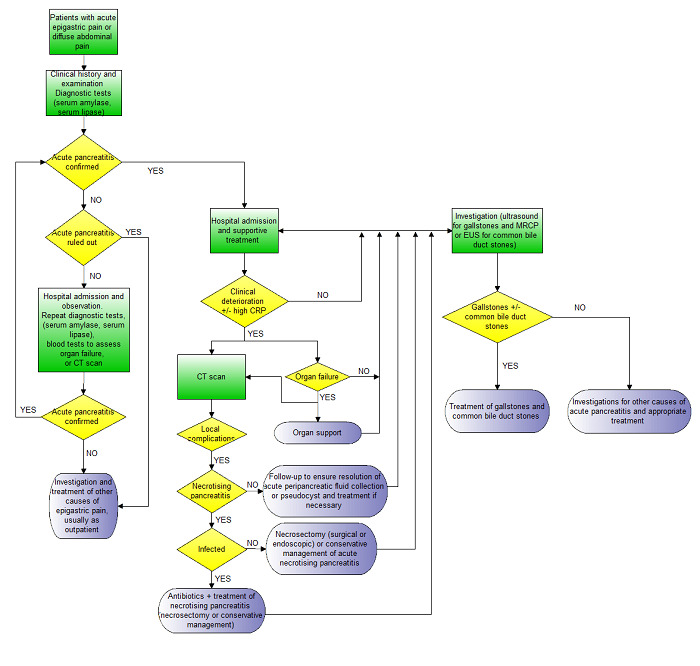
Clinical pathway.
Footnotes:
- Acute pancreatitis is usually confirmed by consensus criteria (Banks 2013).
- Irrespective of the CT scan findings and presence or absence of necrosis, patients with organ failure will require organ support and will receive a CT scan.
- CT scan may also be performed in people without organ failure if there is clinical deterioration (not amounting to organ failure) or in some centres based on an elevated CRP.
- Necrotising pancreatitis is usually confirmed by the findings on the CT scan and by histopathological examination of the biopsy obtained during necrosectomy if early necrosectomy is performed.
- Infected necrotising pancreatitis is usually confirmed by the findings on the CT scan and by microbiological examination of fluid aspirated under radiological guidance or from the tissue biopsy obtained during necrosectomy if early necrosectomy is performed.
- Organ failure is diagnosed on the basis of clinical examination and blood tests (urea, creatinine, blood pressure, pulse rate, respiratory rate, arterial blood gas analysis).
Abbreviations:
CRP: C‐reactive protein CT: computed tomography EUS: endoscopic ultrasound MRCP: magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
