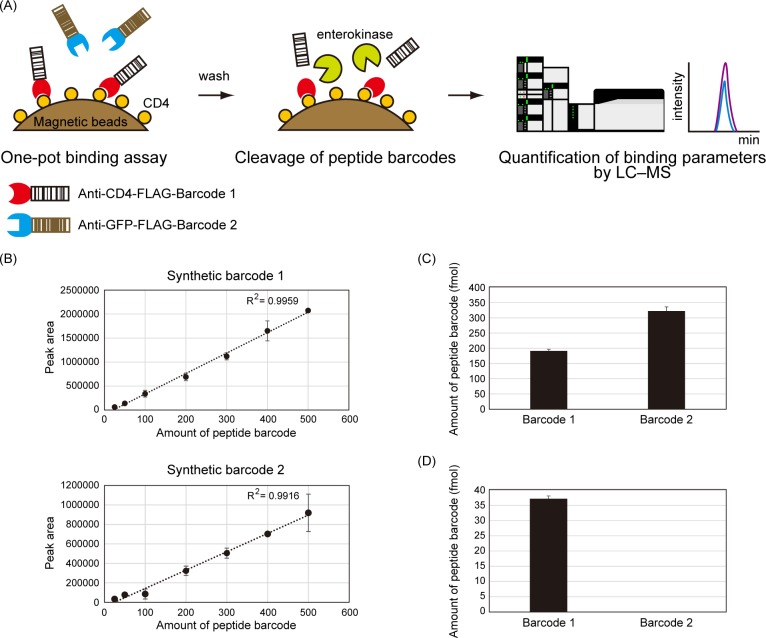
Fig 4. Quantification of binding activities of the barcoded nanobodies by LC–MS.
(A) Experimental scheme to quantify the binding activities of the nanobodies by LC–MS. The barcoded nanobodies are mixed with CD4-coated magnetic beads in one pot, and non-specific nanobodies are washed out. The peptide barcodes are cleaved on beads by a specific protease, enterokinase. Then, eluted peptide barcodes are quantified by mass spectrometry for the evaluation of binding activities. (B) The quantitativity of SRM of each peptide barcode. Synthetic peptide barcodes were serially diluted and quantified by LCMS-8060. Each peptide barcode was successfully analyzed with high sensitivity and quantitativity. Each value represents the mean ± standard deviation of three technical replicates. (C) Quantification of each peptide-barcoded nanobody. The peptide barcodes were cleaved from 250 fmol of each nanobody, and quantified by LCMS-8060. Each value represents the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. (D) Quantification of the binding strength of the peptide-barcoded nanobodies. The amount of nanobodies bound on the CD4-coated magnetic beads was quantified by LCMS-8060. The peptide barcode fused with anti-CD4 nanobody was specifically detected. Each value represents the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments.