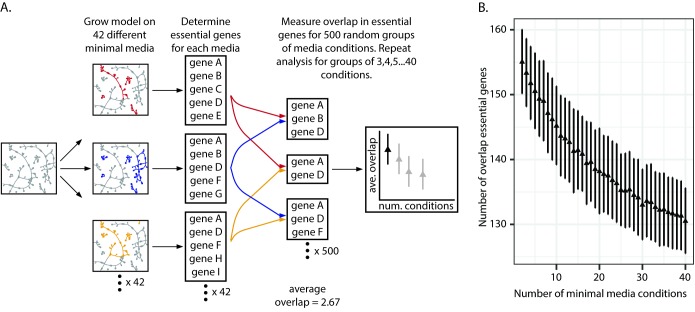
Fig 5. Computational assessment of the impact of number of minimal media conditions considered on condition-independent essentiality.
(A). Pipeline for computational assessment of the impact of minimal media composition on condition-independent essentiality. The base PA14 model is grown on 42 different minimal media. For each minimal media condition, the in silico essential genes are identified, resulting in 42 essential gene lists. Initially, pairwise comparisons are made between minimal media essential gene lists to identify the shared essential genes. Specifically, the essential gene lists from two randomly selected minimal media conditions are compared to determine the overlap between the two gene lists. This random selection of two minimal media conditions to compare is repeated 500 times. The average number of overlap genes for all 500 comparisons is calculated as well as the standard deviation. Ultimately, this random selection of groups of minimal media conditions to compare is repeated for groups of three minimal media conditions, groups of four, and so on, up to groups of 40 minimal media conditions. (B). Impact of minimal media differences on the identification of condition-independent essential genes. Each data point represents the mean from 500 comparisons. Error bars indicate standard deviation.