Figure 2. Mechanisms of Carbon Tetrachloride Hepatotoxicity.
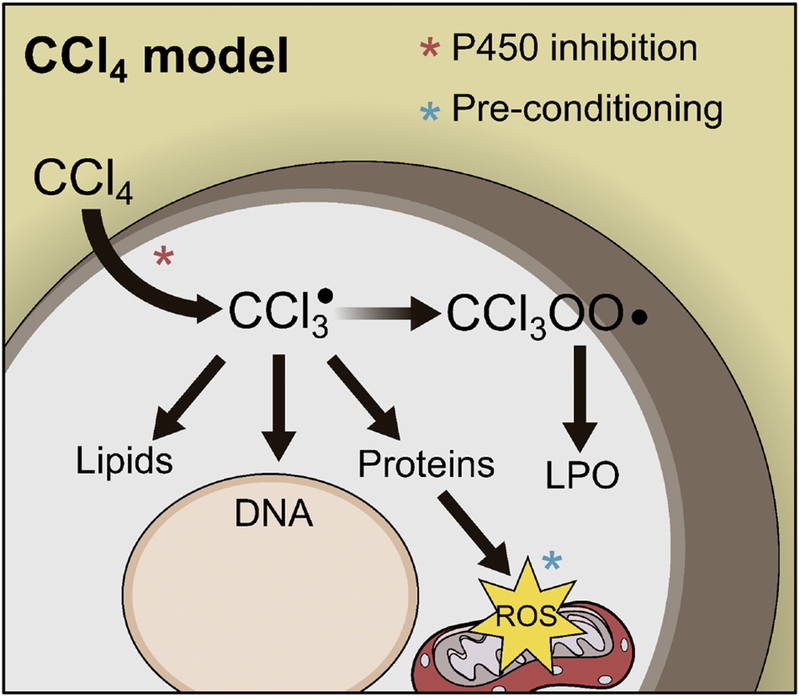
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is converted to a radical (CCl3·) that binds to proteins, DNA and lipids. This causes mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress. CCl3· can also react with O2 to form CCl3OO·, which initiates the lipid peroxidation (LPO) chain reaction that damages cell membranes.
