Figure 3. Importance of Immune Tolerance in Idiosyncratic DILI.
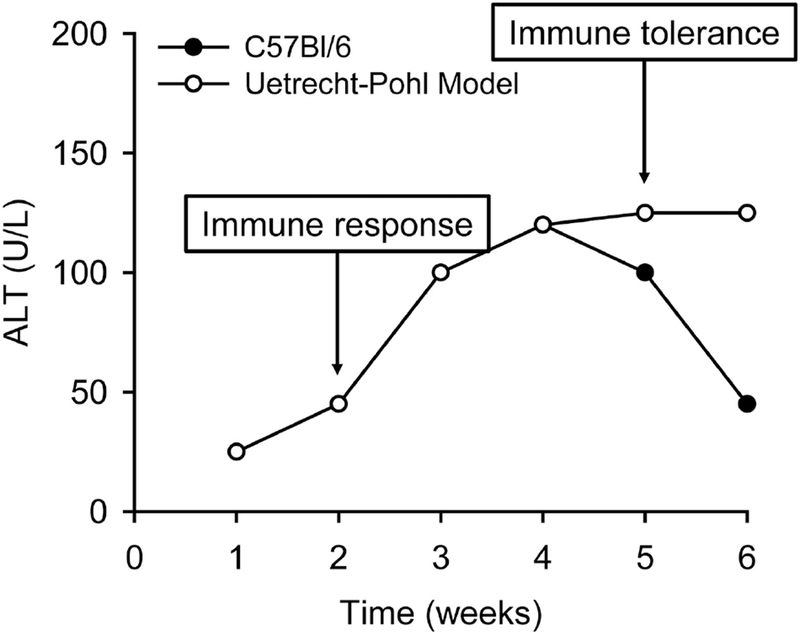
In WT C57Bl/6 mice, daily treatment with idiosyncratic hepatotoxicants causes delayed-onset transient liver injury. In the Uetrecht-Pohl model, various strategies are used to reduce regulation of the adaptive immune system and therefore prevent development of immune tolerance, and those mice experience ongoing liver injury. Results from that model have demonstrated that immune tolerance is a likely explanation for the transient nature of most IDILI in humans; loss of tolerance may explain why only some cases of IDILI are severe.
