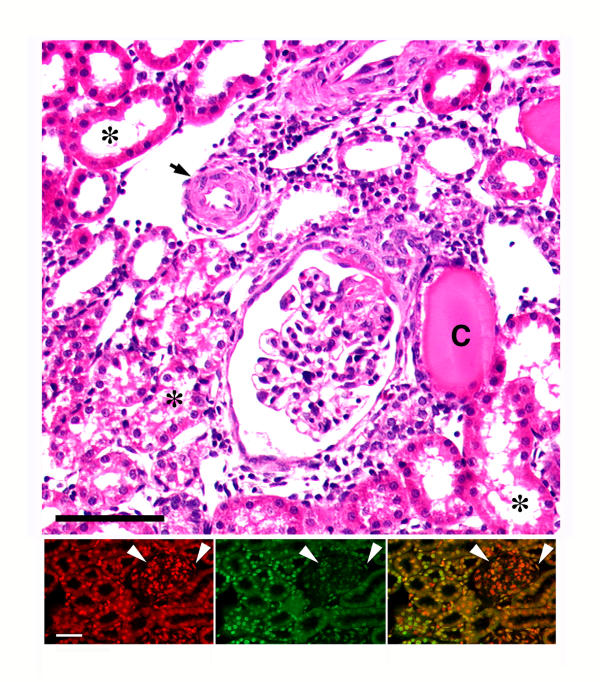
Figure 1.
Representative light micrograph (top panel) of a kidney from an S rat that had been on 8.0% NaCl diet for three weeks. The figure shows typical hypertensive renal lesions, which include thickening of the arteriolar wall (arrow), glomerular sclerosis, and dilatation of tubules with tubular atrophy (asterisks) and presence of cast material (C) in some tubules. Expansion of the interstitium, indicated by an increase in the distance between the tubules, was also evident. H/E stain. Black bar represented 50 μm. The dual immunofluorescent studies at the bottom show how exuberant the apoptotic process can be in this model. The bottom left panel represents a section that was counterstained with propidium iodide to label the nuclei (red color). The middle panel is the same section that was stained using the TUNEL assay, which fluorescein-labels the 3'-OH termini of DNA. Several nuclei in the tubular and glomerular compartments demonstrate the green fluorescence. The bottom right panel is a combined image; the yellow color is the result of overlapping propidium iodide and fluorescein labeling. White bar represented 50 μm. Arrowheads denote glomerulus.