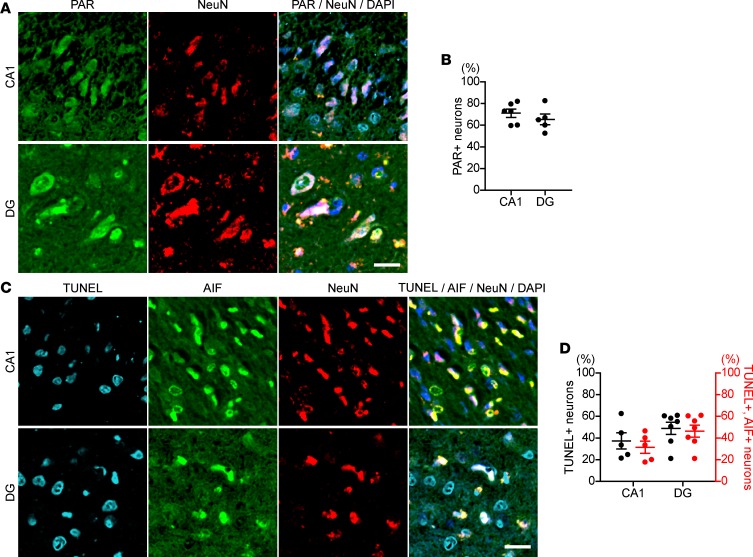
Figure 3. Hippocampal neurons from proband’s deceased sister show an increase in nuclear PAR and AIF-mediated DNA fragmentation.
(A) PAR accumulation in nuclei of hippocampal neurons in the proband’s deceased sister, with homozygous mutation of ARH3. Hippocampal sections were subjected to immunolabeling with anti-PAR (green) and anti-NeuN (red) antibodies. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). CA1, cornu ammonis 1; DG, dentate gyrus. Scale bar: 20 μm. (B) Percentage of PAR-labeled nuclei of neurons in CA1 and DG. Data are mean ± SEM of values obtained from 980 and 426 neurons in CA1 and DG, respectively. (C) AIF translocation to nuclei and DNA fragmentation in hippocampal neurons of the proband’s sister. Brain sections were subjected to TUNEL assay (right blue) and immunolabeling with anti-AIF (green) and NeuN (red) antibodies. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) Percentage of neurons with DNA fragmentation detected by TUNEL assay and AIF translocation to nuclei. Data are mean ± SEM of values obtained 1571 and 1308 neurons in CA1 and DG, respectively.