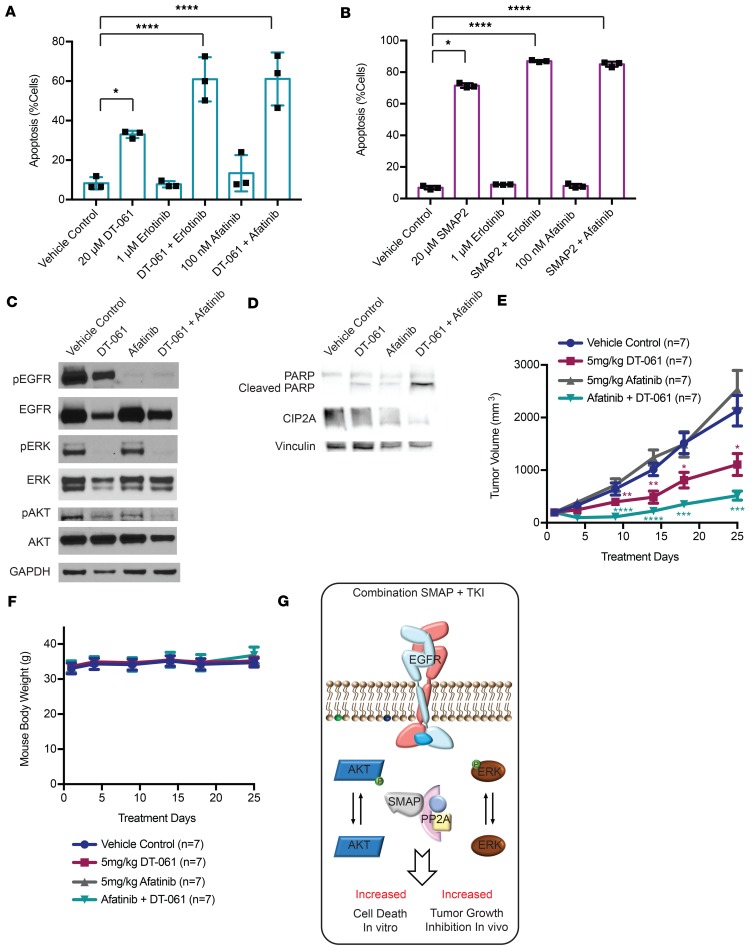
Figure 4. SMAP DT-061 in combination with TKI has an enhanced effect on apoptosis in vitro and tumor growth inhibition in vivo.
(A) H1975 and (B) H1650 cell lines were treated with vehicle control, 20 μM SMAP DT-061, 1 μM erlotinib, 100 nM afatinib, a combination of SMAP DT-061 and erlotinib, or a combination of SMAP DT-061 and afatinib. Annexin positivity at 24 hours in H1975 and H1650 cells treated with indicated concentrations of DT-061. Three independent experiments are represented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. BID: twice daily. (C and D) Western blot analysis of major PP2A and afatinib targets in H1975 treated with 20 μM SMAP DT-061, 100 nM afatinib, or a combination of SMAP DT-061 and afatinib at 24 hours. Results represent 3 independent experiments. (E) H1975 cells (5 million cells per injection) were subcutaneously injected in the right flank of nude mice. Once the tumor volumes reached approximately 100 mm3, mice were randomized and treated with vehicle control (n = 7), SMAP DT-061 (5 mg/kg) (n = 7) twice daily or afatinib (5 mg/kg) (n = 7) twice daily, or a combination of both SMAP DT-061 and afatinib (n = 7). The results are represented as mean ± SEM, with *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. The P values were calculated using a 2-tailed t test. (F) Body weights of mice throughout treatment. (G) Proposed model for enhanced effect of SMAP and TKI treatment of EGFR-driven LUAD. The black asterisks compare the different treatments with the vehicle control. The green asterisks compare the combination of Afatinib and DT-061 group with the vehicle control group, while the purple asterisks compare the DT-061 (5 mg/kg) group with the vehicle control group.