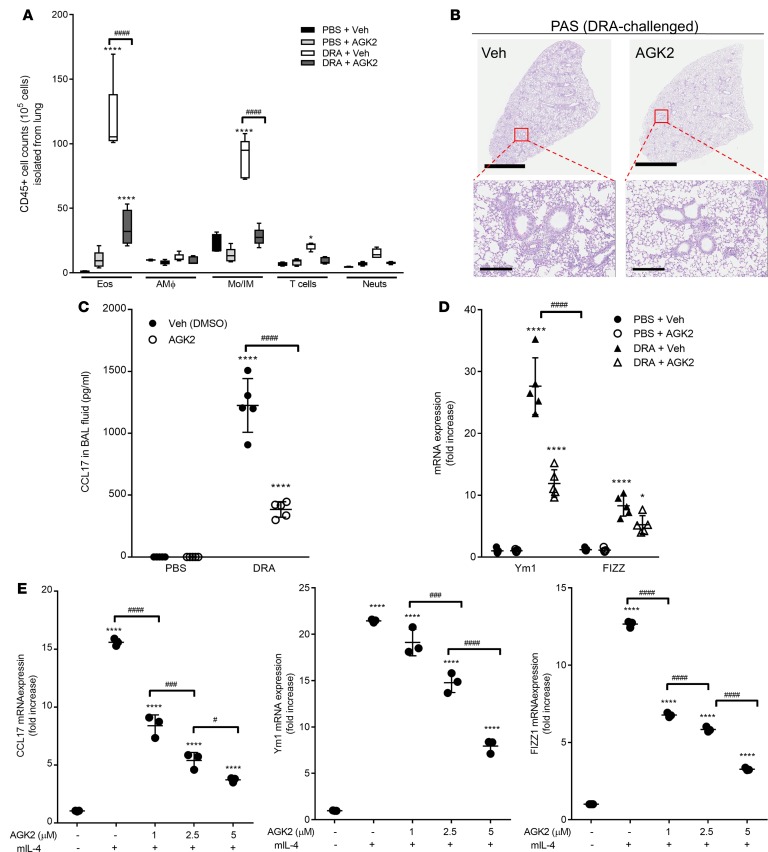
Figure 2. Administration of AGK2, a selective Sirt2 inhibitor, attenuates allergic inflammation by modulating alternative activation of macrophages and CCL17 production.
AGK2 (10 mg/kg; i.p.) was administered 30 minutes prior to DRA challenge on days 12, 13, and 14. (A) Total lung cells were labeled with surface markers for CD45, CD3, CD11c, CD11b, Ly6G, and Siglec F, gated on CD45+ cells, and the percentage of eosinophils, alveolar macrophages, monocytes/interstitial macrophages, T cells, and neutrophils was determined. n = 5 mice/group; analyzed by 1-way ANOVA. (B) Whole lung histological sections were PAS stained. The images are representative of 5 experiments. Scale bar: 3 mm (top); 300 μm (bottom). (C). CCL17 production in BAL fluid was measured by ELISA. n = 5 mice/group; analyzed by 1-way ANOVA. (D) Alternative activation macrophage markers were assessed in whole lung tissue after DRA challenge by qPCR. n = 5 mice/group; analyzed by 1-way ANOVA. (E) Lung macrophages were isolated from WT mice and incubated with rmIL-4 (20 ng/ml) for 24 hours in the presence of AGK2, and expression of CCL17 and alternative activation markers was assessed by qPCR. n = 3 mice/group; analyzed by 1-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.001 when compared with WT control. #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001, ####P < 0.0001 when compared within the groups.