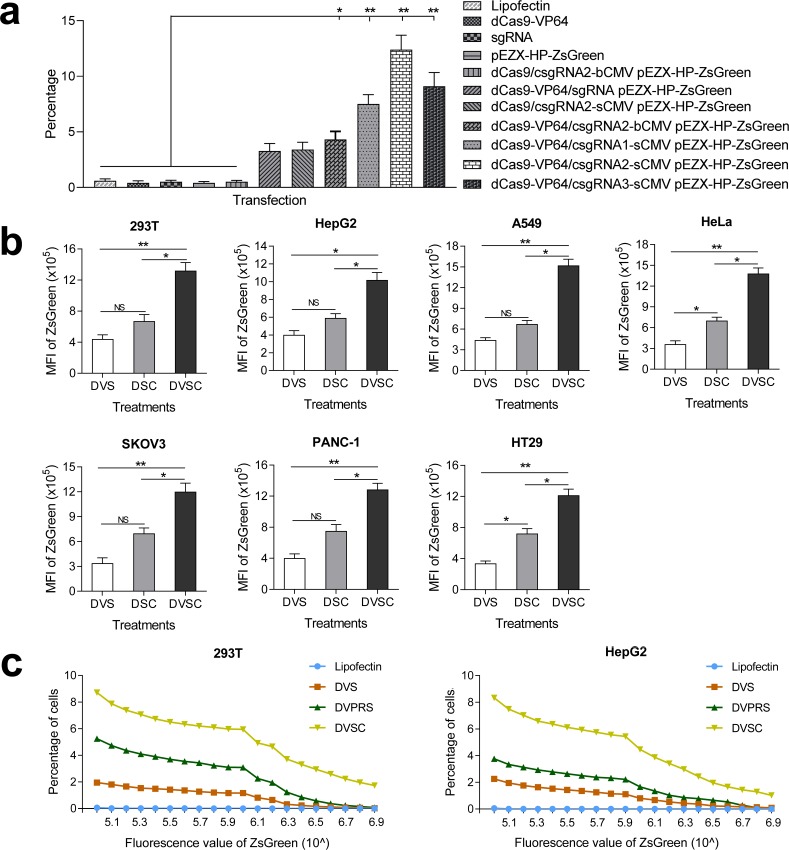
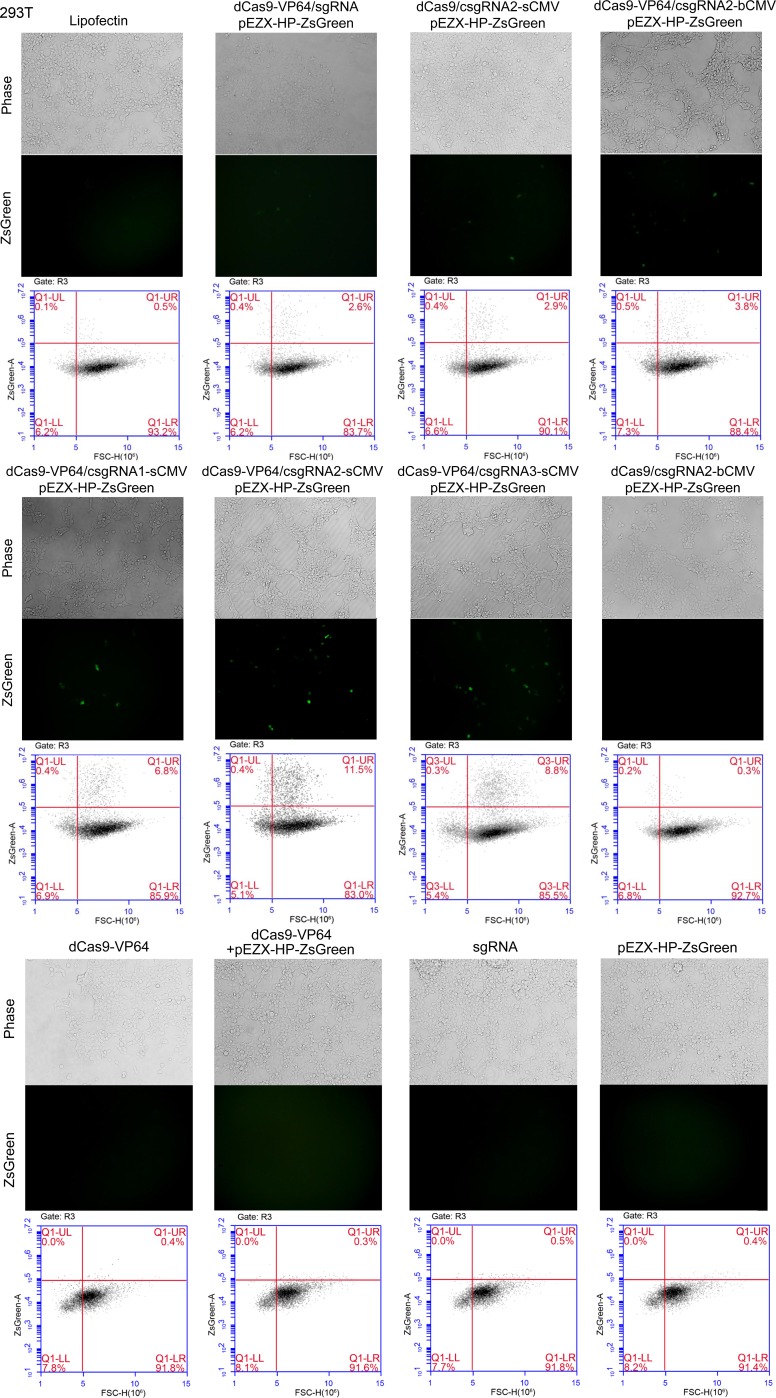
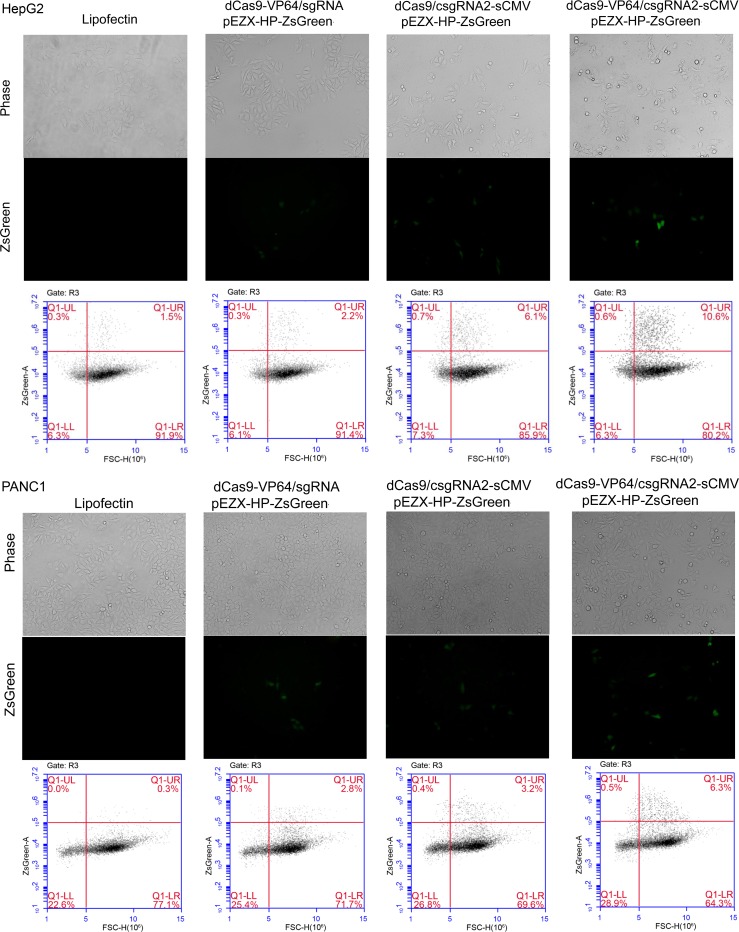
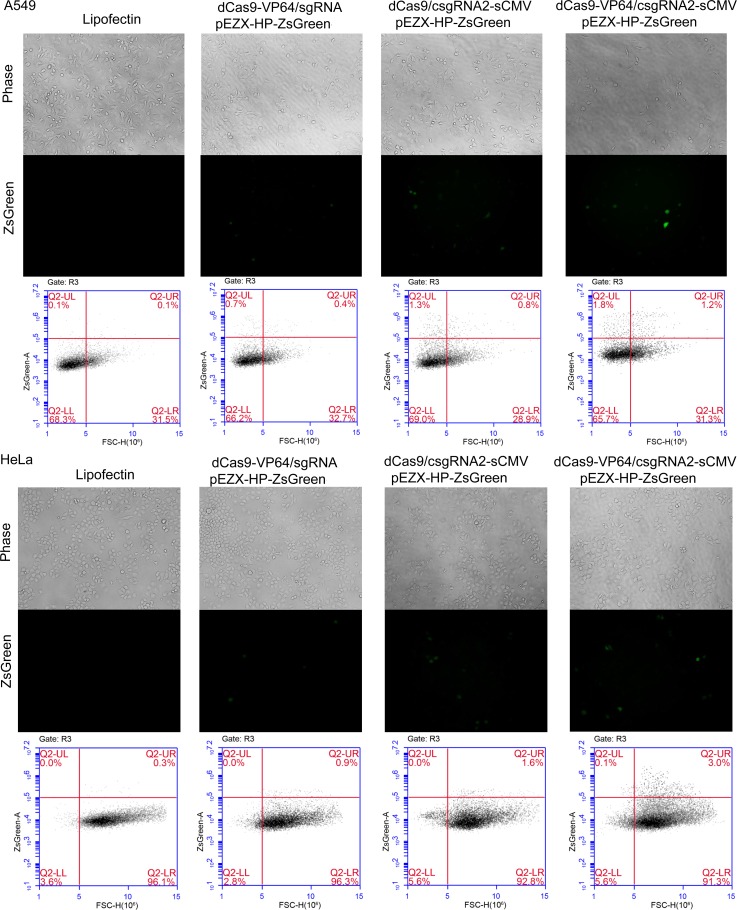
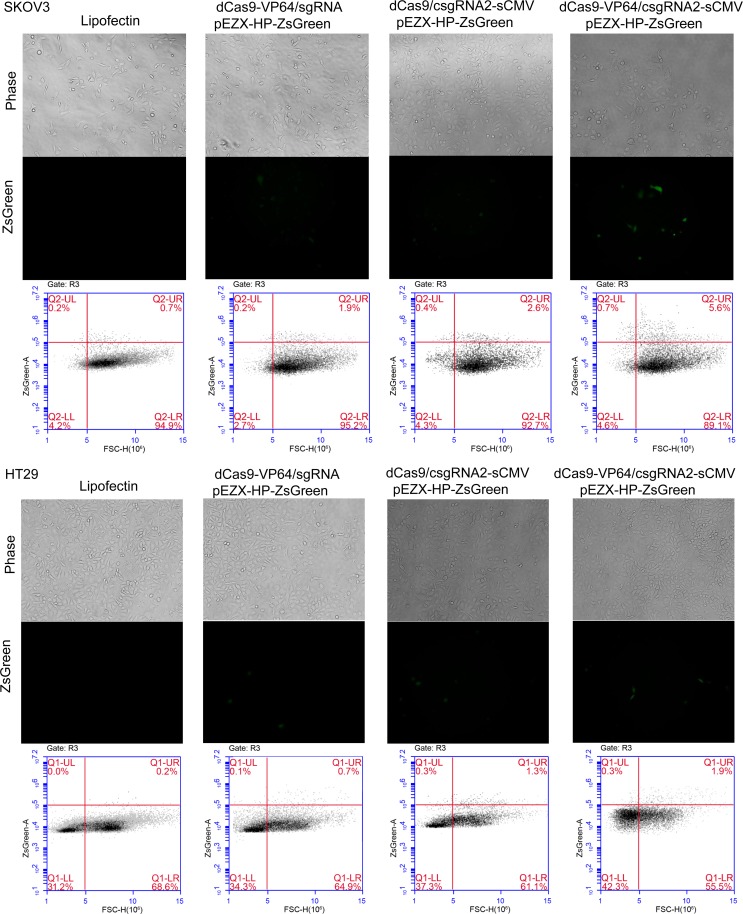
Figure 2. Activation of an exogenous reporter gene ZsGreen under the control of a HNF4α promoter by the CRISPR-assisted trans enhancer in multiple cells.
(a) Transcriptional activation of reporter gene ZsGreen in various cells transfected by different vectors. The florescence intensity of cells was analyzed by flow cytometry and is shown as the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Transfections: DVS, dCas9-VP64/sgRNA; DSC, dCas9/csgRNA-sCMV; DVSC, dCas9-VP64/csgRNA-sCMV. (b) Comparison between trans enhancer and VPR. Cells were transfected with three different transcriptional activation systems to activate reporter gene ZsGreen. The florescence intensity of cells was analyzed by flow cytometry and the number of cells with certain fluorescence intensity was counted. Transfections: Lipo, lipofectin; DVS, dCas9-VP64/sgRNA; DVPRS; dCas9-VPR/csgRNA; DVSC, dCas9-VP64/csgRNA-sCMV.