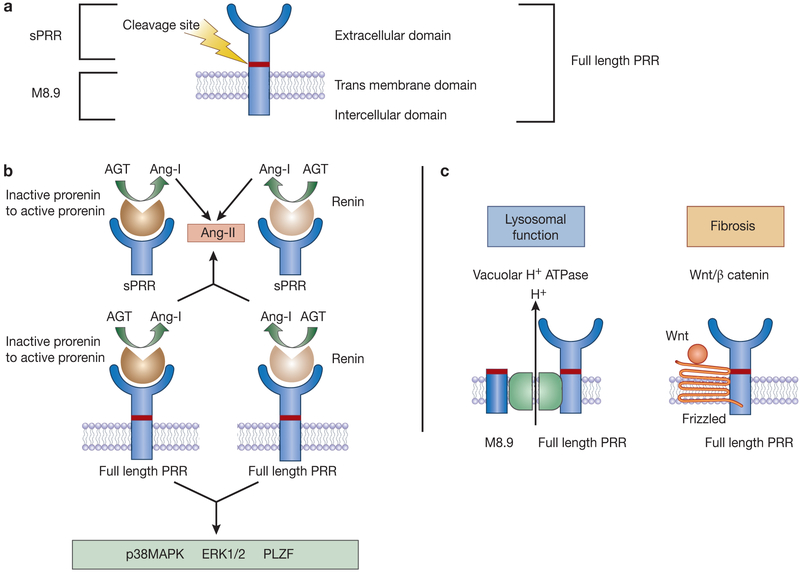
Figure 1.
Basic biology of the (pro)renin receptor (PRR). (A) Simplified schematic of the PRR protein; (B) Prorenin/renin dependent PRR function; and (C) Prorenin/renin independent PRR function. Binding of the prorenin to the full length or sPRR induces non-proteolytic activation of prorenin to cleave angiotensinogen while binding of renin to full length or sPRR increases catalytic efficiency. Independent of Ang-II, binding of prorenin/renin to the PRR activates intra-cellular signaling pathways. AGT – angiotensinogen; Ang-I – angiotensin-I; Ang-II – angiotensin-II; PRR – (pro)renin receptor; sPRR – soluble (pro)renin receptor; p38MAPK – mitogen activated prorenin kinase; ERK1/2 – extracellular signal-regulated kinase; PI3K – phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PLZF – promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger; Wnt/ß catenin.