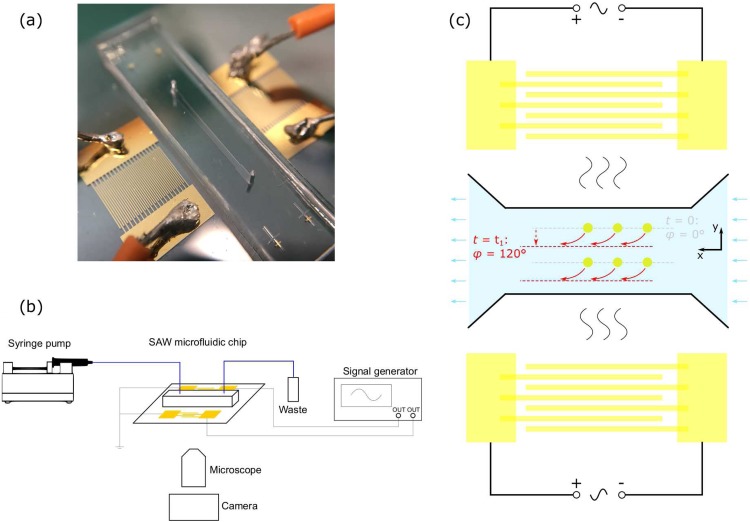
FIG. 1.
(a) Image of the SAW microfluidic chip with two identical interdigital transducers (IDTs) on the LiNbO3 substrate and a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannel between the two IDTs. (b) Schematic of the experimental setup. (c) Schematic of the SAW microfluidic chip and its working mechanism. When t = 0, two input signals are synchronized (relative phase φ = 0), and particles are initially prefocused at the pressure node (gray line). When t = t1, the phase of one IDT is shifted by 120° (relative phase φ = 120°), and the pressure node is immediately translated to a new nodal line (red line), and all the prefocused particles are moved to the new nodal line.