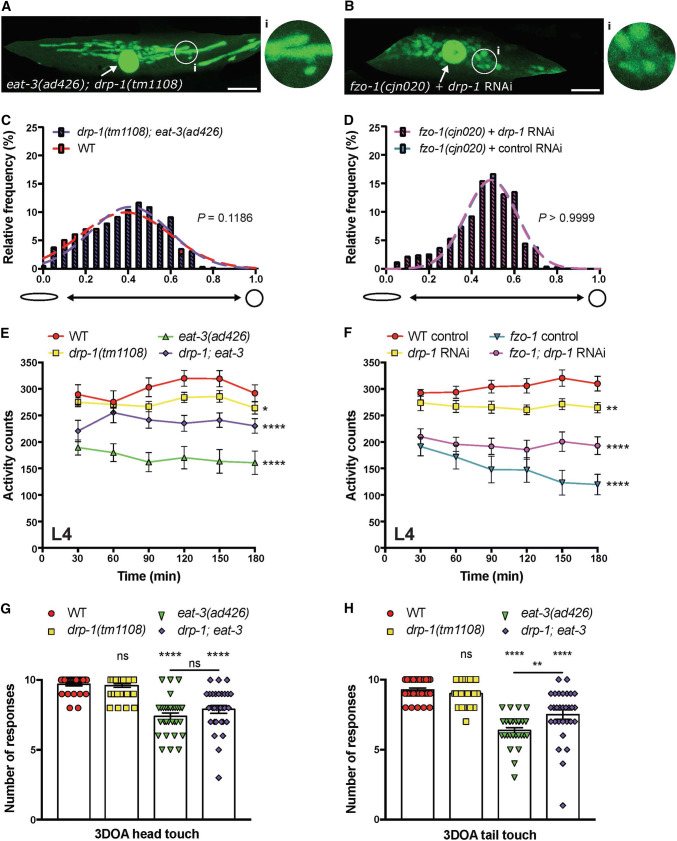
Fig. 7.
Simultaneous disruption of fusion and fission proteins rescues mitochondrial and behavioural phenotypes. Images of a body wall muscle with fluorescently labelled mitochondria (Pmyo-3::MLS::GFP) in a an eat-3(ad426); drp-1(tm1108) double mutant animal and b a fzo-1(cjn020) animal with RNAi knockdown of drp-1. Arrows designate nuclei, which are also labelled with GFP in this transgenic strain. Insets (i) are enlargements (× 3) of the indicated circular areas. Scale bars 20 μm. c, d Histogram and Gaussian distribution of mitochondria circularity scores for eat-3(ad426); drp-1(tm1108) double mutants (c) and fzo-1(cjn020) animals with RNAi knockdown of drp-1 (d). All imaging was performed on L4 stage animals; P values calculated using F tests for variances; n ≥ 1832 mitochondria for quantitative analysis. e, f Quantified movement across populations of L4-stage animals using a WMicrotracker instrument. Data represents the mean ± SEM across ten individual wells; n ≥ 600 worms per genotype. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 compared to WT from one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc tests. g Quantification of anterior mechanosensory neuron function using light touch assays. Symbols represent individual animal responses from three replicate experiments; n ≥ 30 worms. h Quantification of posterior mechanosensory neuron function using the light touch assay; n ≥ 30 worms. Bars represent mean, ± SEM; nsP > 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 from one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc tests for multiple comparisons