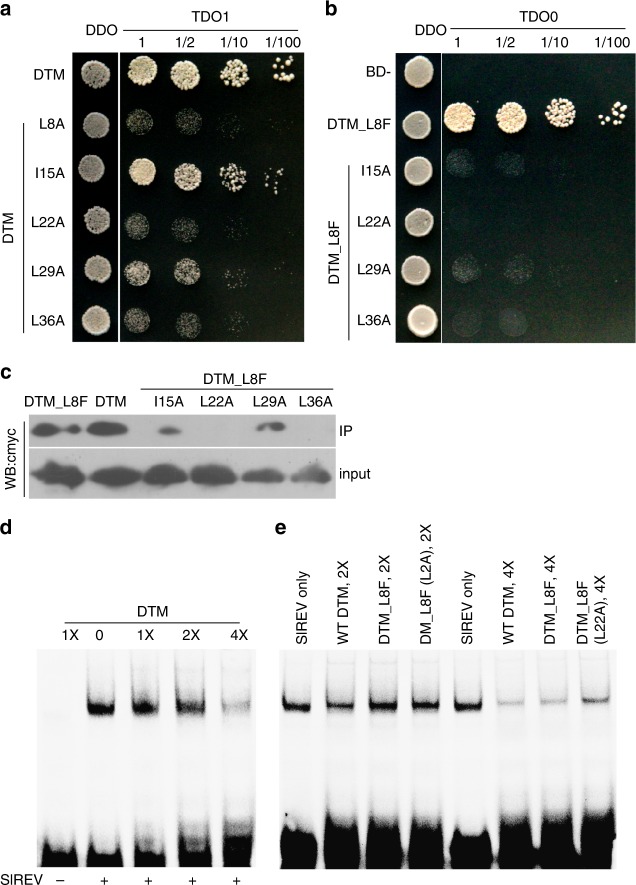
Fig. 5.
Mutagenesis of the DTM protein. a interactions between SlREV (fused to the activation domain, AD) and five DTM mutants with single mutations in the conserved Leu or Ile residues in each heptad (fused to the binding domain, BD) in yeast. The five conserved Leu or Ile residues were individually mutated to Ala. b interactions between SlREV and four DTM double mutants derived from DTM_L8F in yeast. c binding activities of DTM and its mutant forms to its partner, SlREV. DTM and its mutant forms were fused to cmyc and their binding affinities to SlREV (fused to HA) were assayed by pulldown using an anti-HA antibody. d electrophoretic mobility shift assay showing dosage-dependent inhibition of DTM on SlREV binding ability to its target sequence. e inhibitive effect of single and double mutations in the conserved residues of DTM on SlREV binding ability to its target sequence. Both SlREV (1–264 aa) and DTM were synthesized using wheat germ extract, and different concentrations of DTM (d) and/or its mutated forms (e) were tested for their inhibitive effects on SlREV binding to a Cy5-labeled HB9 DNA duplex. 3-AT, 3-amino-1,2,4- triazole; IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot