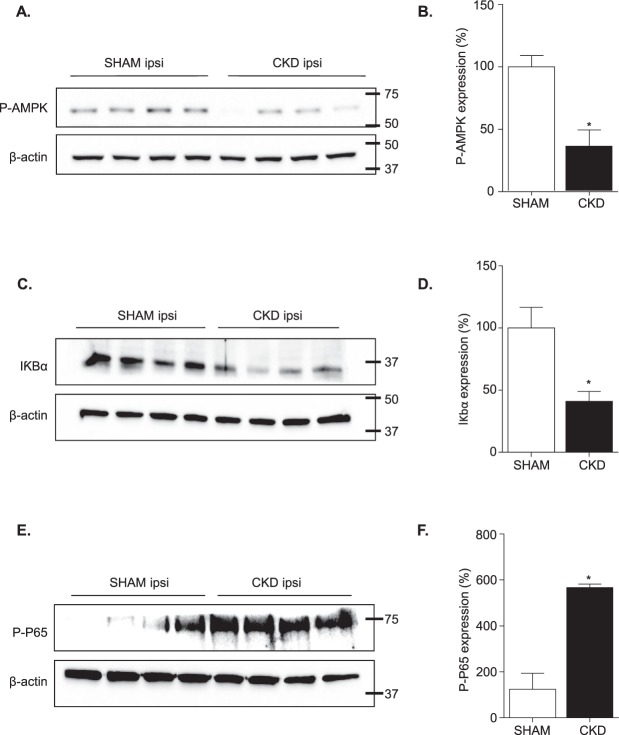
Figure 5.
CKD impairs adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation and promotes canonical NFκB activation. (A and B) Study of AMPK activation. (A) Representative images of the western blot analysis. (B) Quantitative data showing lower AMPK phosphorylation within ischemic hemispheres of CKD mice as compared to SHAM-operated mice. (C and D) Study of IκBα degradation. (C) Representative images of the western blot analysis. (D) Quantitative data showing lower IκBα expression within ischemic hemispheres of CKD mice as compared to SHAM-operated mice. (E and F) Study of p65 phosphorylation. (E) Representative images of the western blot analysis. (F) Quantitative data showing higher phosphorylation of P65 within ischemic hemispheres of CKD mice as compared to SHAM-operated mice. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM and represent data from 4 animals per group. *p < 0.05 CKD versus SHAM mice (non parametric Mann-Whitney U test). Ipsi: ipsilateral hemisphere. Raw western blot data are provided in Supplementary Figs 5, 6 and 7.