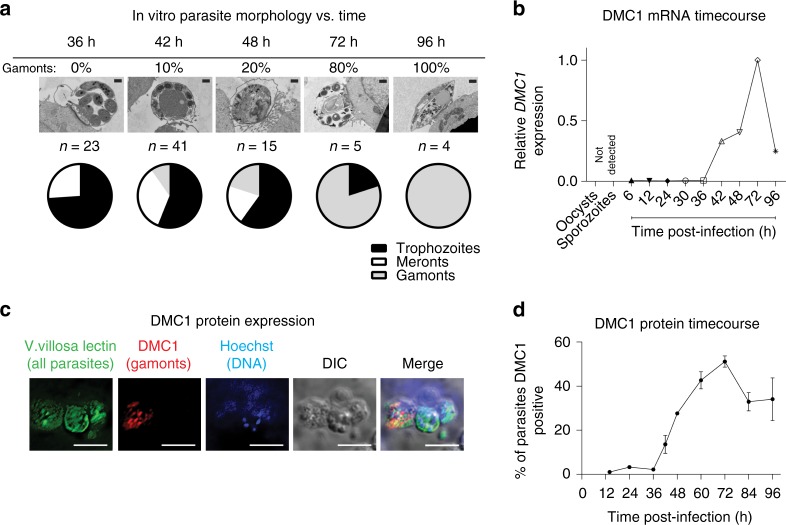
Fig. 5.
DNA Meiotic Recombinase 1 (DMC1) is a biomarker for C. parvum sexual development. a Representative transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images and results of scoring the relative abundance of different C. parvum life cycle stages present versus time after infection of host cell monolayers. Confluent HCT-8 cells were infected with C. parvum for the indicated times before preparing samples for TEM. Scale bar = 500 nm. b C. parvum DMC1 mRNA versus time during HCT-8 cell infection. Wells from the same culture plate as in a were used to isolate RNA, and quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to measure expression of C. parvum DMC1 (cgd7_1690) relative to 18s RNA. Data for a and b are representative of two independent experiments. c Immunofluorescence microscopy showing specific DMC1 expression. A mouse monoclonal anti-C. parvum DMC1 antibody was made and used for immunofluorescence staining and epifluorescence microscopy. DMC1 expression was limited to a subset of parasite vacuoles that contained a single nucleus. Images were acquired 72 h after HCT-8 cell infection (all parasite vacuoles (V. Villosa lectin staining (green)), nuclei (Hoechst (blue)), and anti-DMC1 antibody staining (red)). 60 × oil objective (NA = 1.4); scale bar = 5 µm. Images are representative of two independent experiments. d Time course of DMC1 protein expression. Infected HCT-8 cell monolayers grown in 384-well plates were stained as in c at the indicated time points. Tiled 2 × 2 images (40 × dry objective, NA = 0.7) were used to determine the percent of DMC1 parasites versus time. The graph shows mean and SD for data combined from two biological replicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file