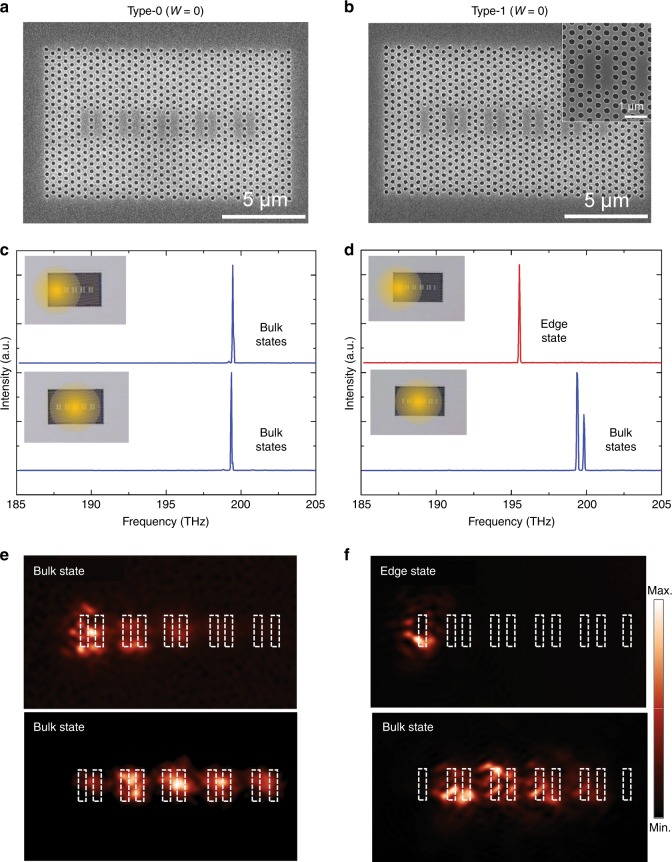
Fig. 3. Implementation and characterisation of the finite photonic Su–Schrieffer–Heeger (SSH) structure.
a, b Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the photonic SSH structures with Type-0 and Type-1 cavities fabricated in an InAsP/InP MQW epilayer. The inset in b shows a magnified SEM image. c, d Micro-photoluminescence spectra obtained from structure Type-0 and Type-1, respectively, with the excitation spot centred at the left edge (top panels) and at the centre (bottom panels) of the device. The insets are used to show the positions of the excitation spot (represented by the yellow-shaded circle) relative to the PhC nanocavity arrays. e, f Near-field scanning optical microscope (NSOM) images recorded for structure Type-0 and Type-1, respectively. The four NSOM images were measured at the corresponding peak emission wavelengths in c, d