Fig. 1.
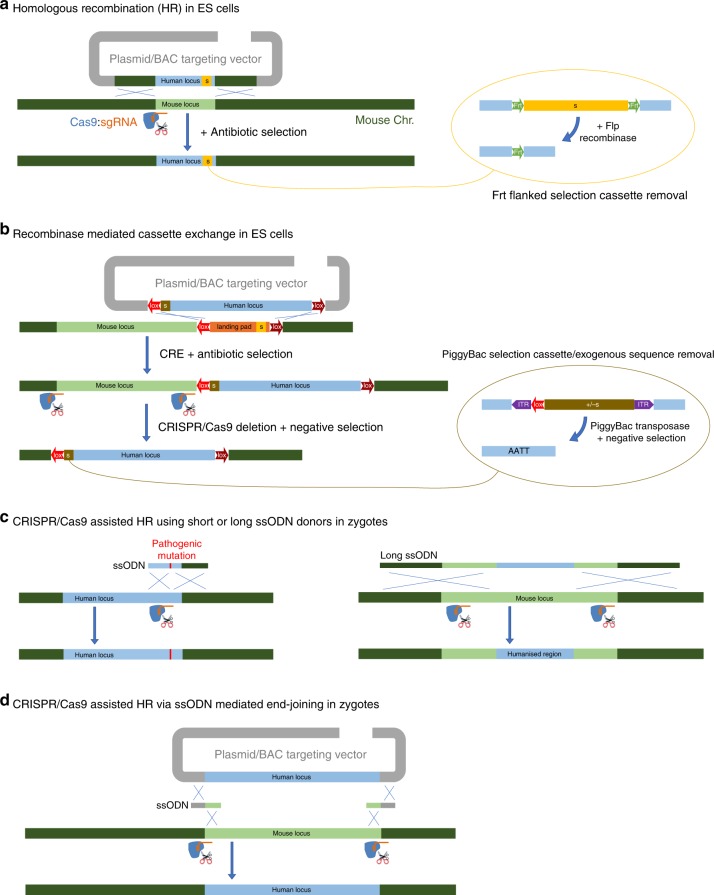
Targeted genomic humanisation technologies. a HR in ES cells has been used to humanise loci up to ~200 kb (and beyond, using iterative targeting). A plasmid, or BAC, targeting vector carrying human sequence flanked by homology arms is transfected into ES cells by electroporation. Addition of Cas9:sgRNA, generating a targeted double strand break, increases HR efficiency. An antibiotic resistance selectable marker is included to enrich for ES cells harbouring the desired recombination. Selection cassettes are commonly flanked by frt sites for later excision by FLP recombinase, leaving a single frt genomic scar. b Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE) can be used to humanise up to ~200 kb loci (can also be employed iteratively). In this example, a landing pad is first inserted at the target locus via HR (see part a), consisting of a selection cassette flanked by heterotypic lox sites. The same lox sites are inserted either side of the orthologous human locus within a BAC vector, which when electroporated into landing pad-harbouring ES cells will recombine in the presence of CRE recombinase. Cas9:sgRNA pairs can subsequently be utilised to delete the mouse locus. As an alternative to FLP/frt recombination, selection cassettes and other exogenous sequences can be flanked by PiggyBac inverted terminal repeats (ITR), which when inserted at an AATT recognition site, leave no genomic scar once excised with PiggyBac transposase. PiggyBAC transposition is less efficient than FLP/frt recombination, thus positive–negative selection cassettes (+/− s) such as HPRT (in HPRT−/− ES) or puroΔTK are used. c Introducing pathogenic mutations into humanised alleles can be achieved by HR in zygotes using a ssODN (~150 bp) donor template combined with a locus-specific Cas9:sgRNA (no selection required). A similar strategy can be used for small-scale humanisation projects (small genes or partial humanisation) using a long ssODN (<2 kb) as a donor template and a pair of Cas9:sgRNAs. d Knock-in of large inserts (up to 200 kb) in both mouse and rat zygotes has been achieved by combining Cas9:sgRNAs and short ssODN donors with hybrid homology at the break-points between donor and target site to facilitate HR