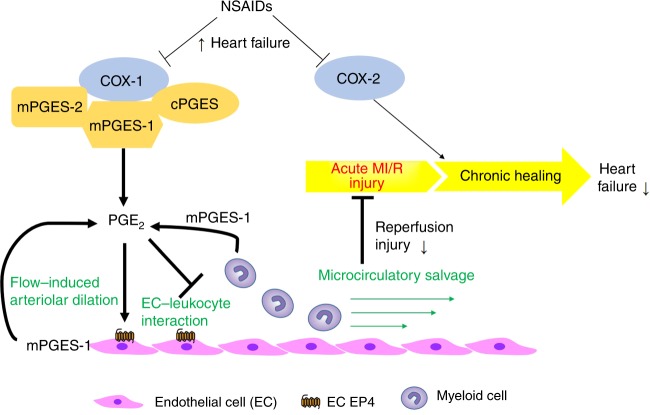
Fig. 8.
Schematic illustration of the role of mPGES-1 and EC EP4 in MI/R. Use of NSAIDs is associated with heart failure. In MI/R related heart failure, the COX pathway protects against development of heart failure through acute protection mainly via COX-1/mPGES-1, as shown in the present study (key components/steps highlighted in bold text), and through chronic healing mainly via COX-2, as shown in previous studies. COX-1, the constitutive COX isoform and mPGES-1 contribute substantially to PGE2 biosynthesis and limit acute MI/R injury. mPGES-1, the major source of PGE2 in endothelial cells and myeloid cells, plays a pivotal role in mediating flow-induced arteriolar dilation and in limiting EC–leukocyte interactions, under I/R. By doing so, mPGES-1 preserves the microcirculation and further constrains MI/R injury. These beneficial effects are mediated in part via endothelial EP4 receptors. → denotes ‘prostanoid production’ or ‘positive regulation’; ┤denotes ‘inhibition’; the thick lines highlight the key findings of this study. cPGES: cytosolic PGE synthase