Fig. 6.
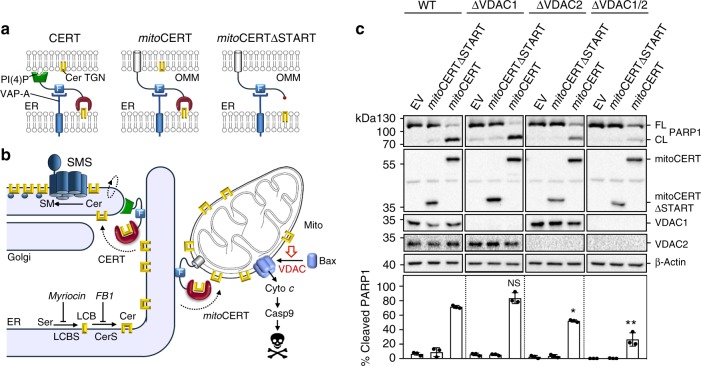
VDAC2 removal disrupts ceramide-induced apoptosis. a Schematic outline of ceramide transfer protein CERT, mitoCERT, and mitoCERTΔSTART. MitoCERT was created by swapping the Golgi-targeting pleckstrin homology domain of CERT against the OMM anchor of AKAP1. Removal of the ceramide transfer or START domain yielded mitoCERTΔSTART. All three proteins bind the ER-resident protein VAP-A via their FFAT motif (F). Cer ceramide, PI(4)P phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate, TGN trans-Golgi network. b Ceramides (Cer) are synthesized through N-acylation of long chain bases (LCB) by ceramide synthases (CerS) on the cytosolic surface of the ER and require CERT-mediated transfer to the Golgi for metabolic conversion into sphingomyelin (SM) by a Golgi-resident SM synthase (SMS). Expression of mitoCERT causes a diversion of this biosynthetic ceramide flow to mitochondria, triggering Bax-dependent apoptosis11. c Wild type (WT), VDAC1-KO (ΔVDAC1), VDAC2-KO (ΔVDAC1), and VDAC1/2 double KO (ΔVDAC1/2) human colon cancer HCT116 cells were transfected with empty vector (EV), Flag-tagged mitoCERT, or Flag-tagged mitoCERTΔSTART. At 24 h post transfection, cells were processed for immunoblotting with antibodies against PARP1, the Flag-epitope, VDAC1, VDAC2, and β-actin. The percentage of PARP1 cleavage was quantified. Data are means ± s.d.; n = 3; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 by two-tailed paired t-test. Source data