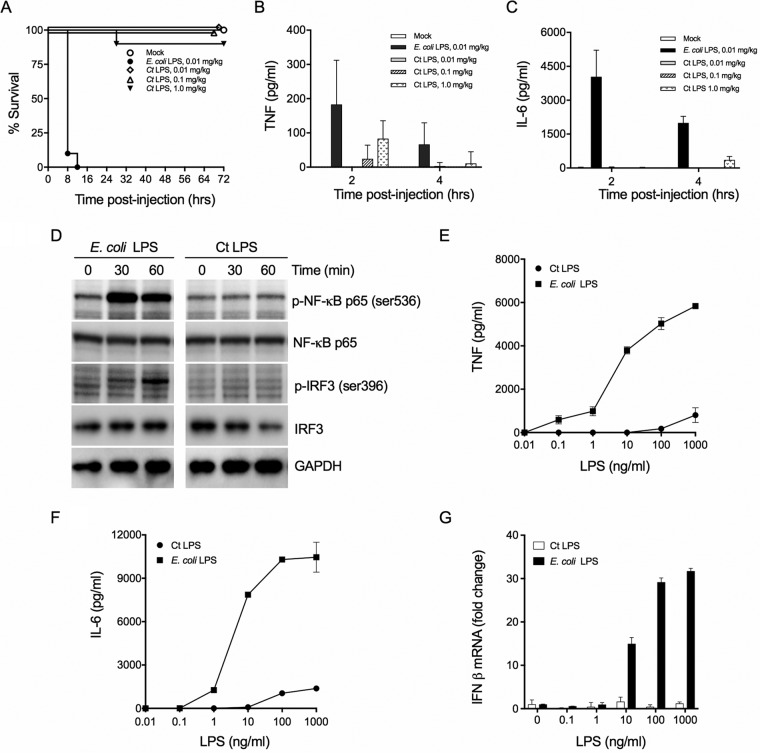
FIG 1.
C. trachomatis (Ct) LPS does not activate the proinflammatory canonical pathway. (A) Mice (n = 5) sensitized with d-GalN were injected i.p. with E. coli or C. trachomatis LPS, and survival was monitored at the indicated times. Five mice per group were injected with LPS. Kaplan-Meier curves were generated by Prism 7. (B and C) Sera were collected at 2 and 4 h postinjection and analyzed by ELISA for TNF (B) and IL-6 (C). (D) Western blot analysis of BMDM treated with E. coli or C. trachomatis LPS (100 ng/ml) at the indicated times. Lysates prepared from BMDM were resolved on SDS-PAGE gels, transferred to PVDF, and immunoblotted with antibodies against NF-κB p65, phospho-NF-κB p65 (ser536), IRF3, p-IRF3 (ser396), and GAPDH. (E and F) BMDM were treated with various LPS concentrations, and the supernatants were collected and analyzed by ELISA for TNF and IL-6, respectively. (G) BMDM were similarly treated with LPS, and IFN-β mRNA was measured by qRT-PCR. Data shown as mean ± SD from three technical replicates (E, F, and G) and representative of three independent experiments (D, E, F, and G).